The internal structure and geodynamics of Mars inferred from a 4.2-Gyr zircon record
- PMID: 33199613
- PMCID: PMC7733809
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2016326117
The internal structure and geodynamics of Mars inferred from a 4.2-Gyr zircon record
Abstract
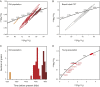
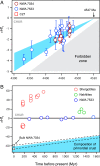
Combining U-Pb ages with Lu-Hf data in zircon provides insights into the magmatic history of rocky planets. The Northwest Africa (NWA) 7034/7533 meteorites are samples of the southern highlands of Mars containing zircon with ages as old as 4476.3 ± 0.9 Ma, interpreted to reflect reworking of the primordial Martian crust by impacts. We extracted a statistically significant zircon population (n = 57) from NWA 7533 that defines a temporal record spanning 4.2 Gyr. Ancient zircons record ages from 4485.5 ± 2.2 Ma to 4331.0 ± 1.4 Ma, defining a bimodal distribution with groupings at 4474 ± 10 Ma and 4442 ± 17 Ma. We interpret these to represent intense bombardment episodes at the planet's surface, possibly triggered by the early migration of gas giant planets. The unradiogenic initial Hf-isotope composition of these zircons establishes that Mars's igneous activity prior to ∼4.3 Ga was limited to impact-related reworking of a chemically enriched, primordial crust. A group of younger detrital zircons record ages from 1548.0 ± 8.8 Ma to 299.5 ± 0.6 Ma. The only plausible sources for these grains are the temporally associated Elysium and Tharsis volcanic provinces that are the expressions of deep-seated mantle plumes. The chondritic-like Hf-isotope compositions of these zircons require the existence of a primitive and convecting mantle reservoir, indicating that Mars has been in a stagnant-lid tectonic regime for most of its history. Our results imply that zircon is ubiquitous on the Martian surface, providing a faithful record of the planet's magmatic history.
Keywords: Mars; geodynamics; meteorites; zircon.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Watson E. B., Harrison M., Zircon saturation revisited: Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 64, 295–304 (1983).
-
- Humayun M., et al. , Origin and age of the earliest Martian crust from meteorite NWA 7533. Nature 503, 513–516 (2013). - PubMed
-
- McCubbin F. M., et al. , Geologic history of Martian regolith breccia Northwest Africa 7034: Evidence for hydrothermal activity and lithologic diversity in the Martian crust. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 121, 2120–2149 (2016).
-
- Hu S., et al. , Ancient geologic events on Mars revealed by zircons and apatites from the Martian regolith breccia NWA 7034. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 54, 850–879 (2019).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

