GIANT: galaxy-based tool for interactive analysis of transcriptomic data
- PMID: 33199699
- PMCID: PMC7670435
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-76769-w
GIANT: galaxy-based tool for interactive analysis of transcriptomic data
Abstract
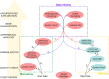
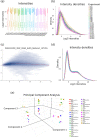
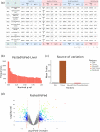
Transcriptomic analyses are broadly used in biomedical research calling for tools allowing biologists to be directly involved in data mining and interpretation. We present here GIANT, a Galaxy-based tool for Interactive ANalysis of Transcriptomic data, which consists of biologist-friendly tools dedicated to analyses of transcriptomic data from microarray or RNA-seq analyses. GIANT is organized into modules allowing researchers to tailor their analyses by choosing the specific set of tool(s) to analyse any type of preprocessed transcriptomic data. It also includes a series of tools dedicated to the handling of raw Affymetrix microarray data. GIANT brings easy-to-use solutions to biologists for transcriptomic data mining and interpretation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Andrews, S. et al.FastQC.http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (2012).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

