Size-dependent strong metal-support interaction in TiO2 supported Au nanocatalysts
- PMID: 33199710
- PMCID: PMC7669859
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19484-4
Size-dependent strong metal-support interaction in TiO2 supported Au nanocatalysts
Abstract
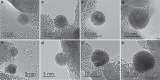
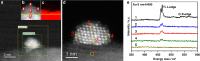
The strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) has long been studied in heterogonous catalysis on account of its importance in stabilizing active metals and tuning catalytic performance. As a dynamic process taking place at the metal-support interface, the SMSI is closely related to the metal surface properties which are usually affected by the size of metal nanoparticles (NPs). In this work we report the discovery of a size effect on classical SMSI in Au/TiO2 catalyst where larger Au particles are more prone to be encapsulated than smaller ones. A thermodynamic equilibrium model was established to describe this phenomenon. According to this finding, the catalytic performance of Au/TiO2 catalyst with uneven size distribution can be improved by selectively encapsulating the large Au NPs in a hydrogenation reaction. This work not only brings in-depth understanding of the SMSI phenomenon and its formation mechanism, but also provides an alternative approach to refine catalyst performance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Tauster SJ, Fung SC, Garten RL. Strong metal-support interactions. Group 8 noble metals supported on titanium dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978;100:170–175. doi: 10.1021/ja00469a029. - DOI
-
- Tauster SJ, Fung SC. Strong metal-support interactions—occurrence among binary oxides of groups Iia-Vb. J. Catal. 1978;55:29–35. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(78)90182-3. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2018M641725/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 51701201/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 21972135/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 21776270/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

