A cellulose synthase-derived enzyme catalyses 3-O-glucuronosylation in saponin biosynthesis
- PMID: 33199711
- PMCID: PMC7669905
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19399-0
A cellulose synthase-derived enzyme catalyses 3-O-glucuronosylation in saponin biosynthesis
Abstract
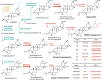
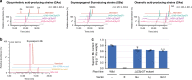
Triterpenoid saponins are specialised metabolites distributed widely in the plant kingdom that consist of one or more sugar moieties attached to triterpenoid aglycones. Despite the widely accepted view that glycosylation is catalysed by UDP-dependent glycosyltransferase (UGT), the UGT which catalyses the transfer of the conserved glucuronic acid moiety at the C-3 position of glycyrrhizin and various soyasaponins has not been determined. Here, we report that a cellulose synthase superfamily-derived glycosyltransferase (CSyGT) catalyses 3-O-glucuronosylation of triterpenoid aglycones. Gene co-expression analyses of three legume species (Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Glycine max, and Lotus japonicus) reveal the involvement of CSyGTs in saponin biosynthesis, and we characterise CSyGTs in vivo using Saccharomyces cerevisiae. CSyGT mutants of L. japonicus do not accumulate soyasaponin, but the ectopic expression of endoplasmic reticulum membrane-localised CSyGTs in a L. japonicus mutant background successfully complement soyasaponin biosynthesis. Finally, we produced glycyrrhizin de novo in yeast, paving the way for sustainable production of high-value saponins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Sparg G, Light E, van Staden J. Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004;94:219–243. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi H, Sudo H. Economic importance of licorice. Plant Biotechnol. 2009;26:101–104.
-
- He J-X, Akao T, Nishino T, Tani T. The influence of commonly prescribed synthetic drugs for peptic ulcer on the pharmacokinetic fate of glycyrrhizin from Shaoyao-Gancao-tang. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001;24:1395–1399. - PubMed
-
- Jeong HG, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury: inhibition of cytochrome P450 2E1 expression. Pharmacol. Res. 2002;46:221–227. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

