Effect of dexmedetomidine combined with etomidate on IL-17A and S-100β expression levels in rats with postoperative cognitive dysfunction
- PMID: 33200000
- PMCID: PMC7664604
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9405
Effect of dexmedetomidine combined with etomidate on IL-17A and S-100β expression levels in rats with postoperative cognitive dysfunction
Abstract
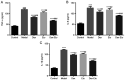
The present study aimed to explore the effects of dexmedetomidine combined with etomidate on the expression levels of interleukin (IL)-17A and S-100β in rats with postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). A total of 50 SD rats were randomly allocated into the control group, model group, etomidate group (Eto group), dexmedetomidine group (Dex group) and dexmedetomidine combined with etomidate group (Dex-Eto group). Inhalation anesthesia was used in all five groups. Apart from the control group, partial lobectomy was performed to construct a rat model of cognitive dysfunction. The rats of the model group received no intravenous anesthesia, except general anesthesia with intubation. Morris water maze test was performed before injection (T0), at the 1st day (T1), the 3rd day (T2) and the 5th day (T3) after operation to assess the memory ability of the rats. At the end of T3, the expression levels of IL-17A, S-100β, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in serum were detected by ELISA and the expression of NF-κB p65 by western blot analysis. Compared with the control group, the model group showed an increased escape latency and swimming distance, decreased number of times of crossing the platform and target quadrant residence time, and increased expression levels of IL-17A, S-100β, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and NF-κB p65. Compared with the model group, the escape latency and swimming distance in the Dex, Eto and Dex-Eto groups were reduced, whereas the number of times of crossing the platform and the target quadrant residence time were increased. In addition, the expression levels of IL-17A, S-100β, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and NF-κB p65 were decreased in the Dex, Eto and Dex-Eto groups, compared with the model group. Among the Dex, Eto and Dex-Eto groups, the escape latency and swimming distance in the Dex-Eto group were the shortest, the number of times of crossing the platform and the target quadrant residence time were the highest, and IL-17A, S-100β, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and NF-κB p65 expression levels were the lowest. In conclusion, dexmedetomidine combined with etomidate can effectively improve POCD.
Keywords: IL-17A; S-100β; dexmedetomidine combined with etomidate; postoperative cognitive dysfunction.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Figures

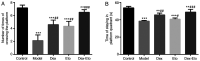
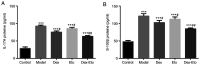


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
