A Novel Topical Ophthalmic Formulation to Mitigate Acute Mustard Gas Keratopathy In Vivo: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 33200047
- PMCID: PMC7645241
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.9.12.6
A Novel Topical Ophthalmic Formulation to Mitigate Acute Mustard Gas Keratopathy In Vivo: A Pilot Study
Abstract
Purpose: This pilot study investigated the in vivo therapeutic potential and tolerability of a multimodal ophthalmic formulation, topical eye drops (TED), for acute mustard gas keratopathy (MGK) using a rabbit model.
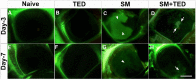
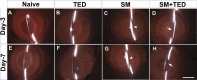
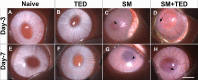
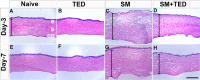
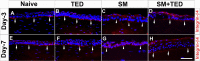
Methods: Twenty New Zealand White rabbits were used. Only right eyes of 18 rabbits (oculus dexter [OD]) received single sulfur mustard gas (SM) vapor injury, whereas contralateral eyes were left untreated or received TED for tolerabilty evaluation. Two rabbit eyes received no treatment and served as age-matched naive control. The four groups were: Naive (oculus sinister [OS] untreated eyes; n = 9); TED (OS treated only with TED BID for 3 days; n = 9); SM (OD exposed to SM vapor; n = 9); and SM+TED (OD exposed to SM+TED BID for 3 days; n = 9). Ocular examination in live rabbits were performed utilizing slit-lamp biomicroscopy, Fantes grading system, fluorescein staining, Schirmer's tests, pachymetry, and applanation tonometry. Cellular and molecular changes in rabbit corneas were assessed after humane euthanasia on day-3 and day-7 with histopathological and real-time polymerase chain reaction PCR techniques.
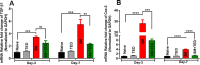
Results: TED to rabbit eyes was found tolerable in vivo. SM-exposed eyes showed significant increase in Fantes scores, central corneal thickness (CCT), Schirmer's test, epithelium-stroma separation, and corneal edema. TED mitigated clinical symptoms by reducing corneal edema, Fantes scores, CCT, and Schirmer's test. Further, TED decreased SM-induced corneal haze, inflammatory and profibrotic markers, transforming growth factor-TGF-β1 and cyclooxygenase-2COX-2, and damage to corneal structure, including epithelial-stromal integrity.
Conclusions: The developed multimodal eyedrop formulation, TED, has potential to mitigate acute MGK effectively in vivo.
Translational relevance: TED is effective against MGK.
Keywords: cornea; corneal edema; intraocular pressure; ocular inflammation; sulfur mustard.
Copyright 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: R. Tripathi, None; P.K. Balne, None; N.R. Sinha, None; L.M. Martin, None; S. Kamil, None; J.R. Landreneau, None; S. Gupta, None; J.T. Rodier, None; P.R. Sinha, None; N.P. Hesemann, None; A.C. Hofmann, None; M.K. Fink, None; S.S. Chaurasia, None; R.R. Mohan, None
Figures


References
-
- Wattana M, Bey T. Mustard gas or sulfur mustard: an old chemical agent as a new terrorist threat. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2009; 24: 19–29. - PubMed
-
- Kilic E, Ortatatli M, Sezigen S, Eyison RK, Kenar L. Acute intensive care unit management of mustard gas victims: the Turkish experience. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2018; 37: 332–337. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg MI, Sexton KJ, Vearrier D. Sea-dumped chemical weapons: environmental risk, occupational hazard. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016; 54: 79–91. - PubMed
-
- Renshaw B. Observation on the role of water in the susceptibility of human skin to injury by vesicant vapors. J Invest Dermatol. 1947; 9: 75–85. - PubMed
-
- Emad A, Rezaian GH.. Immunoglobulins and cellular constituents of the BAL fluid of patients with sulfur mustard gas-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 1999; 115: 346–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

