Inhalable Nanoparticles/Microparticles of an AMPK and Nrf2 Activator for Targeted Pulmonary Drug Delivery as Dry Powder Inhalers
- PMID: 33200330
- PMCID: PMC7669792
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-020-00531-3
Inhalable Nanoparticles/Microparticles of an AMPK and Nrf2 Activator for Targeted Pulmonary Drug Delivery as Dry Powder Inhalers
Abstract
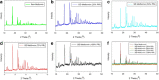
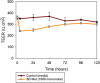
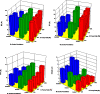
Metformin is an activator of the AMPK and Nrf2 pathways which are important in the pathology of several complex pulmonary diseases with unmet medical needs. Organic solution advanced spray drying in the absence of water in closed-mode was used to design and develop respirable dry powders. Following comprehensive characterization, the influence of physicochemical properties was correlated with performance as aerosols using inertial impaction and three different human dry powder inhaler (DPI) devices varying in device properties. In vitro cell assays were conducted to test safety in 2D human pulmonary cell lines and in 3D small airway epithelia comprising primary cells at the air-liquid interface (ALI). In addition, in vitro transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) was carried out. Metformin remained crystalline following advanced spray drying under these conditions. All SD powders consisted of nanoparticles/microparticles in the solid state. In vitro aerosol dispersion performance showed high aerosolization for all SD metformin powders with all DPI devices tested. High emitted dose for all powders with all three DPI devices was measured. Differences in other aerosol performance parameters and the interplay between the properties of different formulations produced at specific pump rates and the three different DPI devices were correlated with spray drying pump rate and device properties. Safety over a wide metformin dose range was also demonstrated in vitro. Aerosol delivery of metformin nanoparticles/microparticles has the potential to be a new "first-in-class" therapeutic for the treatment of a number of pulmonary diseases including pulmonary vascular diseases such as pulmonary hypertension.
Keywords: 2D/3D human lung cell cultures; advanced spray drying; in vitro; nanotechnology; respiratory drug delivery.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Advanced therapeutic inhalation aerosols of a Nrf2 activator and RhoA/Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitor for targeted pulmonary drug delivery in pulmonary hypertension: design, characterization, aerosolization, in vitro 2D/3D human lung cell cultures, and in vivo efficacy.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021 Jan-Dec;15:1753466621998245. doi: 10.1177/1753466621998245. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021. PMID: 33719747 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of l-Carnitine and l-Carnitine HCL salt for targeted lung treatment of pulmonary hypertension (PH) as inhalation aerosols: Design, comprehensive characterization, in vitro 2D/3D cell cultures, and in vivo MCT-Rat model of PH.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Dec;65:101998. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2021.101998. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 33556627 Free PMC article.
-
Design, characterization, and aerosol dispersion performance modeling of advanced spray-dried microparticulate/nanoparticulate mannitol powders for targeted pulmonary delivery as dry powder inhalers.J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2014 Apr;27(2):81-93. doi: 10.1089/jamp.2013.1078. Epub 2014 Feb 6. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 24502451 Free PMC article.
-
Spray-Dried Inhalable Powder Formulations of Therapeutic Proteins and Peptides.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021 Jun 18;22(5):185. doi: 10.1208/s12249-021-02043-5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021. PMID: 34143327 Review.
-
Solid state of inhalable high dose powders.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Oct;189:114468. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114468. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35917868 Review.
Cited by
-
The role and mechanism of AMPK in pulmonary hypertension.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024 Jan-Dec;18:17534666241271990. doi: 10.1177/17534666241271990. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2024. PMID: 39136335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-Based Inhalation Therapy for Pulmonary Diseases.Curr Drug Metab. 2022;23(11):882-896. doi: 10.2174/1389200223666220803103039. Curr Drug Metab. 2022. PMID: 35927812
-
Tuning the Emulsion Properties Influences the Size of Poly(Caprolactone) Particles for Drug Delivery Applications.AAPS J. 2023 Oct 27;25(6):100. doi: 10.1208/s12248-023-00869-4. AAPS J. 2023. PMID: 37891411
-
Formoterol PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles Induce Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Renal Proximal Tubules.AAPS J. 2021 Jun 24;23(4):88. doi: 10.1208/s12248-021-00619-4. AAPS J. 2021. PMID: 34169439 Free PMC article.
-
Target Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 in Pulmonary Hypertension: Molecular Insight into Application.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jun 6;2022:7845503. doi: 10.1155/2022/7845503. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35707273 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acosta MF, Hayes DJ, Fineman JR, Yuan JX-J, Black SM, Mansour HM. Book chapter 19: therapeutics in pulmonary hypertension. In: Hickey AJ, Mansour HM, editors. Inhalation aerosols: physical and biological basis for therapy. 3. London: CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2019. pp. 313–322.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

