Low dose of ROSuvastatin in combination with EZEtimibe effectively and permanently reduce low density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration independently of timing of administration (ROSEZE): A randomized, crossover study - preliminary results
- PMID: 33200812
- PMCID: PMC8105047
- DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2020.0166
Low dose of ROSuvastatin in combination with EZEtimibe effectively and permanently reduce low density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration independently of timing of administration (ROSEZE): A randomized, crossover study - preliminary results
Abstract
Background: In an attempt to improve low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) level control in patients ineffectively treated with statins, we evaluated the effectiveness of a fixed-dose combination (FDC) of 10 mg rosuvastatin and ezetimibe and its relation to the timing of drug administration.
Methods: A randomized, open label, single center, crossover study involving 83 patients with coronary artery disease and hypercholesterolemia with baseline LDL-C ≥ 70 mg/dL. In arm I the FDC drug was administered in the morning for 6 weeks, then in the evening for the following 6 weeks and vice versa in arm II. The primary endpoint was the change in LDL-C after 6 and 12 weeks.
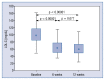
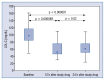
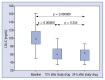
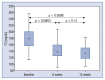
Results: The median LDL-C concentration at baseline, after 6 and 12 weeks respectively was: 98.10 mg/dL (Q1;Q3: 85.10;116.80), 63.14 mg/dL (50.70;77.10) and 59.40 mg/dL (49.00;73.30); p < 0.001. LDL-C levels were similar regardless of the timing of drug administration (morning 62.50 mg/dL [50.70;76.00] vs. evening 59.70 mg/dL [48.20;73.80]; p = 0.259], in both time points: 6 week: 63.15 mg/dL (50.75;80.65) vs. 63.40 mg/dL (50.60;74.00), p = 0.775; and 12 week: 62.00 mg/dL (50.20;74.40) vs. 59.05 mg/dL (47.65;66.05), p = 0.362. The absolute change in LDL-C concentration for the morning vs. evening drug administration was - 6 week: -34.6 mg/dL (-56.55; -19.85) (-34.87%) vs. -31.10 mg/dL (-44.20; -16.00) (-35.87%) (p not significant); 12. week: -34.20 mg/dL (-47.8; -19.0) (-37.12%) vs. -37.20 mg/dL (-65.55; -23.85) (-40.06%) (p not significant). The therapy was safe and well tolerated.
Conclusions: Fixed-dose combination of rosuvastatin and ezetimibe significantly and permanently decreases LDL-C regardless of the timing of drug administration.
Keywords: adherence; apolipoprotein B; fixed-dose; hypercholesterolemia; lipoprotein(a); secondary prevention; timing of administration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The impact of the time of drug administration on the effectiveness of combined treatment of hypercholesterolemia with Rosuvastatin and Ezetimibe (RosEze): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2017 Jul 11;18(1):316. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2047-8. Trials. 2017. PMID: 28697767 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Fixed-dose Combination of Low-intensity Rosuvastatin and Ezetimibe Versus Moderate-intensity Rosuvastatin Monotherapy on Lipid Profiles in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia: A Randomized, Double-blind, Multicenter, Phase III Study.Clin Ther. 2021 Sep;43(9):1573-1589. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.07.016. Epub 2021 Aug 21. Clin Ther. 2021. PMID: 34429197 Clinical Trial.
-
A Phase III, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, Active Comparator Clinical Trial to Compare the Efficacy and Safety of Combination Therapy With Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin Versus Rosuvastatin Monotherapy in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia: I-ROSETTE (Ildong Rosuvastatin & Ezetimibe for Hypercholesterolemia) Randomized Controlled Trial.Clin Ther. 2018 Feb;40(2):226-241.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.12.018. Clin Ther. 2018. PMID: 29402522 Clinical Trial.
-
Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe: A Review in Hypercholesterolemia.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2020 Aug;20(4):381-392. doi: 10.1007/s40256-020-00421-1. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32648167 Review.
-
An overview of rosuvastatin/ezetimibe association for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Apr;21(5):531-539. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1714028. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32036729 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetic comparison of a fixed-dose combination of telmisartan/rosuvastatin/ezetimibe/amlodipine 80/20/10/5 mg and a loose-dose combination of ezetimibe/rosuvastatin 10/20 mg and telmisartan/amlodipine 80/5 mg in healthy male subjects.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):9139-9150. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03863-z. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39907783 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of rosuvastatin alone or in combination with fenofibrate or omega-3 fatty acids on lipoprotein(a) levels in patients with mixed hyperlipidemia.Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis. 2024 Feb 19;9:e26-e32. doi: 10.5114/amsad/178441. eCollection 2024. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis. 2024. PMID: 38434941 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Effectiveness of Rosuvastatin-Ezetimibe Single Pill (Rovazet®) in Korean Dyslipidemia Patients.J Clin Med. 2025 Aug 4;14(15):5480. doi: 10.3390/jcm14155480. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40807110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2018;39:119–177. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx393. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Catapano A, Graham I, De Backer G, et al. 2016 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias. The Task Force for the Management of Dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Developed with the special contribution of the European Assocciation for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR) Eur Heart J. 2016;37(39):2999–3058. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw272.. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

