Combined onabotulinumtoxinA/atogepant treatment blocks activation/sensitization of high-threshold and wide-dynamic range neurons
- PMID: 33200944
- PMCID: PMC7786391
- DOI: 10.1177/0333102420970507
Combined onabotulinumtoxinA/atogepant treatment blocks activation/sensitization of high-threshold and wide-dynamic range neurons
Abstract
Background: OnabotulinumtoxinA and agents that block calcitonin gene‒receptor peptide action have both been found to have anti-migraine effects, but they inhibit different populations of meningeal nociceptors. We therefore tested the effects of combined treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA and the calcitonin gene‒receptor peptide antagonist atogepant on activation/sensitization of trigeminovascular neurons by cortical spreading depression.
Material and methods: Single-unit recordings were obtained of high-threshold and wide-dynamic-range neurons in the spinal trigeminal nucleus, and cortical spreading depression was then induced in anesthetized rats that had received scalp injections of onabotulinumtoxinA 7 days earlier and intravenous atogepant infusion 1 h earlier. The control group received scalp saline injections and intravenous vehicle infusion.
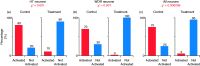
Results: OnabotulinumtoxinA/atogepant pretreatment prevented cortical spreading depression-induced activation and sensitization in both populations (control: Activation in 80% of high-threshold and 70% of wide-dynamic-range neurons, sensitization in 80% of high-threshold and 60% of wide-dynamic-range neurons; treatment: activation in 10% of high-threshold and 0% of wide-dynamic-range neurons, sensitization in 0% of high-threshold and 5% of wide-dynamic-range neurons).
Discussion: We propose that the robust inhibition of high-threshold and wide-dynamic-range neurons by the combination treatment was achieved through dual blockade of the Aδ and C classes of meningeal nociceptors. Combination therapy that inhibits meningeal C-fibers and prevents calcitonin gene‒receptor peptide from activating its receptors on Aδ-meningeal nociceptors may be more effective than a monotherapy in reducing migraine days per month in patients with chronic migraine.
Keywords: CGRP; Migraine; cortical spreading depression; headache; meningeal nociceptor; trigeminal.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Atogepant - an orally-administered CGRP antagonist - attenuates activation of meningeal nociceptors by CSD.Cephalalgia. 2022 Aug;42(9):933-943. doi: 10.1177/03331024221083544. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Cephalalgia. 2022. PMID: 35332801 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insight into atogepant mechanisms of action in migraine prevention.Brain. 2024 Aug 1;147(8):2884-2896. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae062. Brain. 2024. PMID: 38411458 Free PMC article.
-
Fremanezumab-A Humanized Monoclonal Anti-CGRP Antibody-Inhibits Thinly Myelinated (Aδ) But Not Unmyelinated (C) Meningeal Nociceptors.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 1;37(44):10587-10596. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2211-17.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 29. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28972120 Free PMC article.
-
Atogepant for Migraine Prevention: A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Safety.Clin Drug Investig. 2022 Apr;42(4):301-308. doi: 10.1007/s40261-022-01130-0. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Clin Drug Investig. 2022. PMID: 35230651
-
Atogepant: Mechanism of action, clinical and translational science.Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Jan;17(1):e13707. doi: 10.1111/cts.13707. Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38266063 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights from 25 years of onabotulinumtoxinA in migraine - mechanisms and management.Nat Rev Neurol. 2024 Sep;20(9):555-568. doi: 10.1038/s41582-024-01002-5. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Nat Rev Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39160284 Review.
-
Oral atogepant mitigates spreading depolarization-induced pain and anxiety behavior in mice.J Headache Pain. 2025 Aug 21;26(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s10194-025-02125-w. J Headache Pain. 2025. PMID: 40841621 Free PMC article.
-
Breaking the cycle: unraveling the diagnostic, pathophysiological and treatment challenges of refractory migraine.Front Neurol. 2023 Sep 27;14:1263535. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1263535. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37830088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world effectiveness, satisfaction, and optimization of ubrogepant for the acute treatment of migraine in combination with onabotulinumtoxinA: results from the COURAGE Study.J Headache Pain. 2023 Aug 3;24(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01622-0. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 37537578 Free PMC article.
-
Gepants: Key Features of A Potent Therapeutic Option and Considerations in The Latin American Context.Rev Neurol. 2025 Jun 25;80(5):38637. doi: 10.31083/RN38637. Rev Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40613410 Free PMC article. Review. English.
References
-
- Mayberg M, Langer RS, Zervas NT, et al. Perivascular meningeal projections from cat trigeminal ganglia: Possible pathway for vascular headaches in man. Science 1981; 213: 228–230. - PubMed
-
- May A, Goadsby PJ. The trigeminovascular system in humans: Pathophysiologic implications for primary headache syndromes of the neural influences on the cerebral circulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1999; 19: 115–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

