Emerging cellular and molecular determinants of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 33201251
- PMCID: PMC7669490
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-020-03693-7
Emerging cellular and molecular determinants of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
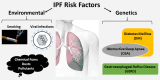
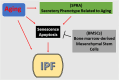
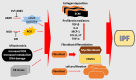
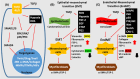
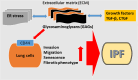
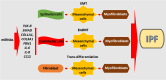
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), the most common form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia, is a progressive, irreversible, and typically lethal disease characterized by an abnormal fibrotic response involving vast areas of the lungs. Given the poor knowledge of the mechanisms underpinning IPF onset and progression, a better understanding of the cellular processes and molecular pathways involved is essential for the development of effective therapies, currently lacking. Besides a number of established IPF-associated risk factors, such as cigarette smoking, environmental factors, comorbidities, and viral infections, several other processes have been linked with this devastating disease. Apoptosis, senescence, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, endothelial-mesenchymal transition, and epithelial cell migration have been shown to play a key role in IPF-associated tissue remodeling. Moreover, molecules, such as chemokines, cytokines, growth factors, adenosine, glycosaminoglycans, non-coding RNAs, and cellular processes including oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum stress, hypoxia, and alternative polyadenylation have been linked with IPF development. Importantly, strategies targeting these processes have been investigated to modulate abnormal cellular phenotypes and maintain tissue homeostasis in the lung. This review provides an update regarding the emerging cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the onset and progression of IPF.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cell plasticity; Chemokines; Cytokines; EMT; EndMT; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Molecular pathways; Senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jones MG, Fabre A, Schneider P, Cinetto F, Sgalla G, Mavrogordato M, Jogai S, Alzetani A, Marshall BG, O'Reilly KM, Warner JA, Lackie PM, Davies DE, Hansell DM, Nicholson AG, Sinclair I, Brown KK, Richeldi L. Three-dimensional characterization of fibroblast foci in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. JCI Insight. 2016 doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.86375. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collard HR, Moore BB, Flaherty KR, Brown KK, Kaner RJ, King TE, Jr, Lasky JA, Loyd JE, Noth I, Olman MA, Raghu G, Roman J, Ryu JH, Zisman DA, Hunninghake GW, Colby TV, Egan JJ, Hansell DM, Johkoh T, Kaminski N, Kim DS, Kondoh Y, Lynch DA, Muller-Quernheim J, Myers JL, Nicholson AG, Selman M, Toews GB, Wells AU, Martinez FJ. Acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176(7):636–643. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200703-463PP. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

