The "hype" of hydrops in classifying vestibular disorders: a narrative review
- PMID: 33201310
- PMCID: PMC7718205
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-020-10278-8
The "hype" of hydrops in classifying vestibular disorders: a narrative review
Abstract
Background: Classifying and diagnosing peripheral vestibular disorders based on their symptoms is challenging due to possible symptom overlap or atypical clinical presentation. To improve the diagnostic trajectory, gadolinium-based contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the inner ear is nowadays frequently used for the in vivo confirmation of endolymphatic hydrops in humans. However, hydrops is visualized in both healthy subjects and patients with vestibular disorders, which might make the clinical value of hydrops detection on MRI questionable.
Objective: To investigate the diagnostic value of clinical and radiological features, including the in vivo visualization of endolymphatic hydrops, for the classification and diagnosis of vestibular disorders.
Methods: A literature search was performed in February and March 2019 to estimate the prevalence of various features in healthy subjects and in common vestibular disorders to make a graphical comparison between healthy and abnormal.
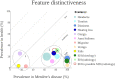
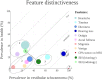
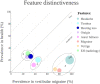
Results: Of the features studied, hydrops was found to be a highly prevalent feature in Menière's disease (99.4%). Though, hydrops has also a relatively high prevalence in patients with vestibular schwannoma (48.2%) and in healthy temporal bones (12.5%) as well. In patients diagnosed with (definite or probable) Menière's disease, hydrops is less frequently diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging compared to the histological confirmation (82.3% versus 99.4%). The mean prevalence of radiologically diagnosed hydrops was 31% in healthy subjects, 28.1% in patients with vestibular migraine, and 25.9% in patients with vestibular schwannoma. An interesting finding was an absolute difference in hydrops prevalence between the two diagnostic techniques (histology and radiology) of 25.2% in patients with Menière's disease and 29% in patients with vestibular schwannoma.
Conclusions: Although the visualization of hydrops has a high diagnostic value in patients with definite Menière's disease, it is important to appreciate the relatively high prevalence of hydrops in healthy populations and other vestibular disorders. Endolymphatic hydrops is not a pathognomic phenomenon, and detecting hydrops should not directly indicate a diagnosis of Menière's disease. Both symptom-driven and hydrops-based classification systems have disadvantages. Therefore, it might be worth to explore features "beyond" hydrops. New analysis techniques, such as Radiomics, might play an essential role in (re)classifying vestibular disorders in the future.
Keywords: Disease; Distinctiveness; Endolymphatic hydrops; Magnetic resonance imaging; Menière’s; Symptoms; Vestibular disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the review was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Visualization of endolymphatic hydrops and correlation with audio-vestibular functional testing in patients with definite Meniere's disease.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2013 Apr;40(2):167-72. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2012.07.009. Epub 2012 Aug 4. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2013. PMID: 22867525
-
The vestibular aqueduct ossification on temporal bone CT: an old sign revisited to rule out the presence of endolymphatic hydrops in Menière's disease patients.Eur Radiol. 2020 Nov;30(11):6331-6338. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06980-w. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32537729
-
[Visualization of endolymphatic hydrops in 3D-FLAIR MRI after intratympanic Gd-DTPA administration in Meniere's disease patients].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Aug;48(8):628-33. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24195817 Chinese.
-
[Clinical significance of radiological methods for diagnosing endolymphatic hydrops in Ménière's disease].Vestn Otorinolaringol. 2021;86(5):82-89. doi: 10.17116/otorino20218605182. Vestn Otorinolaringol. 2021. PMID: 34783479 Review. Russian.
-
What is Menière's disease? A contemporary re-evaluation of endolymphatic hydrops.J Neurol. 2016 Apr;263 Suppl 1:S71-81. doi: 10.1007/s00415-015-7930-1. Epub 2016 Apr 15. J Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27083887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in Elderly Patients With Menière's Disease.Otol Neurotol Open. 2023 Jun 15;3(2):e034. doi: 10.1097/ONO.0000000000000034. eCollection 2023 Jun. Otol Neurotol Open. 2023. PMID: 38516125 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric Properties of a 17-Item German Language Short Form of the Speech, Spatial, and Qualities of Hearing Scale and Their Correlation to Audiometry in 97 Individuals with Unilateral Menière's Disease from a Prospective Multicenter Registry.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 13;14(14):4953. doi: 10.3390/jcm14144953. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725646 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Imaging of the Vestibular Endolymphatic Space in Ménière's Disease.Front Surg. 2021 Aug 23;8:700271. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.700271. eCollection 2021. Front Surg. 2021. PMID: 34497826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced Eye Velocity in Head Impulse Testing-A Possible Indicator of Endolymphatic Hydrops.Front Surg. 2021 May 7;8:666390. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.666390. eCollection 2021. Front Surg. 2021. PMID: 34026816 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous Delayed Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Imaging of the Endolymphatic Space: A Methodological Comparative Study.Front Neurol. 2021 Apr 22;12:647296. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.647296. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33967941 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

