The neurotoxic effect of isoflurane on age-defined neurons generated from tertiary dentate matrix in mice
- PMID: 33201600
- PMCID: PMC7821555
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1949
The neurotoxic effect of isoflurane on age-defined neurons generated from tertiary dentate matrix in mice
Abstract
Introduction: Recent animal studies showed that isoflurane exposure may lead to the disturbance of hippocampal neurogenesis and later cognitive impairment. However, much less is known about the effect of isoflurane exposure on the neurons generated form tertiary dentate matrix, even though a great increase of granule cell population during the infantile period is principally derived from this area.
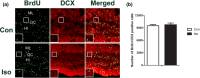
Methods: To label the new cells originated from the tertiary dentate matrix, the mice were injected with BrdU on postnatal day 6 (P6). Then, the mice were exposed to isoflurane for 4 hr at 1, 8, 21, and 42 days after BrdU injection, and the brains were collected 24 hr later. The loss of newly generated cells/neurons with different developmental stage was assessed by BrdU, BrdU + DCX, BrdU + NeuN, or BrdU + Prox-1 staining, respectively.
Results: We found that the isoflurane exposure significantly decreased the numbers of nascent cells (1 day old) and mature neurons (42 days old), but had no effect on the immature (8 days old) and early mature neurons (8 and 21 days old, respectively).
Conclusion: The results suggested isoflurane exposure exerts the neurotoxic effects on the tertiary dentate matrix-originated cells with an age-defined pattern in mice, which partly explain the cognitive impairment resulting from isoflurane exposure to the young brain.
Keywords: anesthetics; isoflurane; neurotoxicity; tertiary dentate matrix.
© 2020 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Andropoulos, D. B. (2018). Effect of anesthesia on the developing brain: Infant and fetus. Fetal Diagnosis and Therapy, 43(1), 1–11. - PubMed
-
- Brandt, M. D. , Jessberger, S. , Steiner, B. , Kronenberg, G. , Reuter, K. , Bick‐Sander, A. , von der Behrens, W. , & Kempermann, G. (2003). Transient calretinin expression defines early postmitotic step of neuronal differentiation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis of mice. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 24(3), 603–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

