Next-Generation Hardware Advances in CT: Cardiac Applications
- PMID: 33201793
- PMCID: PMC7771994
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020192791
Next-Generation Hardware Advances in CT: Cardiac Applications
Abstract
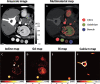
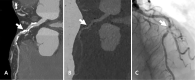
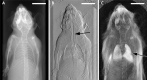
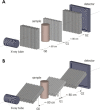
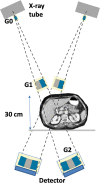
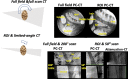
Impending major hardware advances in cardiac CT include three areas: ultra-high-resolution (UHR) CT, photon-counting CT, and phase-contrast CT. Cardiac CT is a particularly demanding CT application that requires a high degree of temporal resolution, spatial resolution, and soft-tissue contrast in a moving structure. In this review, cardiac CT is used to highlight the strengths of these technical advances. UHR CT improves visualization of calcified and stented vessels but may result in increased noise and radiation exposure. Photon-counting CT uses multiple photon energies to reduce artifacts, improve contrast resolution, and perform material decomposition. Finally, phase-contrast CT uses x-ray refraction properties to improve spatial and soft-tissue contrast. This review describes these hardware advances in CT and their relevance to cardiovascular imaging.
© RSNA, 2020.
Figures


References
-
- Schmidt B, Grant K, Flohr TG, Allmendinger T. Cardiac CT Platforms: State of the Art. In: Schoepf UJ, ed. CT of the Heart. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Humana/Springer, 2019; 51–67.
-
- Flohr TG, Allmendinger T, Bruder H, Schwemmer C, Kappler S, Schmidt B. Future Technological Advances in Cardiac CT. In: Schoepf UJ, ed. CT of the Heart. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Humana/Springer, 2019; 873–892.
-
- Schoepf UJ, ed. CT of the Heart. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Humana/Springer, 2019.
-
- Dodge JT, Jr, Brown BG, Bolson EL, Dodge HT. Lumen diameter of normal human coronary arteries. Influence of age, sex, anatomic variation, and left ventricular hypertrophy or dilation. Circulation 1992;86(1):232–246. - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi A, Argulian E, Leipsic J, Newby DE, Narula J. From Subclinical Atherosclerosis to Plaque Progression and Acute Coronary Events: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;74(12):1608–1617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

