Outcome of transcatheter aortic valve replacement in bicuspid aortic valve stenosis with new-generation devices
- PMID: 33201993
- PMCID: PMC8906794
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivaa231
Outcome of transcatheter aortic valve replacement in bicuspid aortic valve stenosis with new-generation devices
Abstract
Objectives: To compare device success and paravalvular leak rates of 3 new-generation transcatheter aortic valve replacement devices in patients with bicuspid aortic valve stenosis and to test their biomechanical performance in a computer-based simulation model of aortic root with increasing ellipticity.
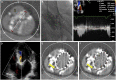
Methods: This retrospective multicentre study included 56 bicuspid aortic valve patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement with new-generation devices: Lotus/Lotus Edge (N = 15; 27%), Evolut-R (N = 20; 36%) and ACURATE neo (N = 21; 37%). Three virtual simulation models of aortic root with increasing index of eccentricity (0-0.25-0.5) were implemented. Stress distribution, stent-root contact area and paravalvular orifice area were computed.
Results: Device success was achieved in 43/56 patients (77%) with comparable rates among Lotus (87%), Evolut-R (60%) and ACURATE neo (86%; P = 0.085). Moderate paravalvular leak rate was significantly lower in the Lotus group as compared to Evolut-R group (0% vs 30%; P = 0.027) and comparable to the ACURATE neo group (0% vs 10%; P = 0.33). By index of eccentricity = 0.5, Lotus showed a uniform and symmetric pattern of stress distribution with absent paravalvular orifice area, ACURATE neo showed a mild asymmetry with small paravalvular orifice area (1.1 mm2), whereas a severely asymmetric pattern was evident with Evolut-R, resulting in a large paravalvular orifice area (12.0 mm2).
Conclusions: Transcatheter aortic valve replacement in bicuspid aortic valve patients with new-generation devices showed comparable device success rates. Lotus showed moderate paravalvular leak rate comparable to that of ACURATE neo and significantly lower than Evolut-R. On simulation, Lotus and ACURATE neo showed optimal adaptability to elliptic anatomies as compared to Evolut-R.
Keywords: Bicuspid aortic valve; Computational simulation; New-generation devices; Transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Mack MJ, Leon MB, Thourani VH, Makkar R, Kodali SK, Russo M et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a balloon-expandable valve in low-risk patients. N Engl J Med 2019;380:1695–705. - PubMed
-
- Yoon SH, Lefèvre T, Ahn JM, Perlman GY, Dvir D, Latib A et al. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement with early- and new-generation devices in bicuspid aortic valve stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;68:1195–205. - PubMed
-
- Perlman GY, Blanke P, Webb JG. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation in bicuspid aortic valve stenosis. EuroIntervention 2016;12:Y42–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

