MicroRNA-574-5p Attenuates Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Targeting HMGB1
- PMID: 33202146
- PMCID: PMC7874400
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0112OC
MicroRNA-574-5p Attenuates Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Targeting HMGB1
Abstract
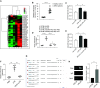
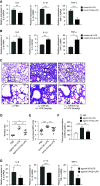
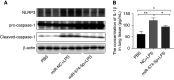
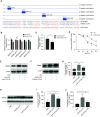
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a critical condition with high mortality. HMGB1 (high-mobility group protein B1) is one of the key proinflammatory factors in the ARDS "inflammatory storm." According to previous studies, some microRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in this process. We aimed to determine the contributing miRNAs targeting the expression and release of HMGB1. miRNA expression in the peripheral blood of patients with ARDS was measured by miRNA microarray. miRNAs targeting HMGB1 were screened and explored for further study. In LPS-induced cell and mouse ARDS models, we explored the effect of this miRNA on the expression and secretion of HMGB1 by Western blot, real-time qPCR, and ELISA. The effects of this miRNA on the NF-κB signaling pathway, proinflammatory cytokines, and NLRP3 (nod-like receptor protein 3) inflammasome were detected by Western blot and real-time qPCR. In ARDS models, microRNA-574-5p (miR-574-5p) expression could be induced by the TLR4/NF-κB pathway upon LPS stimulation. It could suppress the inflammatory response by targeting HMGB1. Enforcing the expression of miR-574-5p or HMGB1 siRNA silencing inhibits the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Moreover, overexpression of HMGB1 reversed the antiinflammatory effect of miR-574-5p. In ARDS mice, overexpression of miR-574-5p suppresses alveolar leukocytes infiltration, interstitial edema, protein effusion, and inflammation. This study demonstrated that miR-574-5p provided negative feedback to LPS-induced inflammation and relieved ARDS. It may provide new therapeutic strategies for ARDS.
Keywords: HMGB1; NF-κB; NLRP3 inflammasome; miR-574-5p.
Figures


Comment in
-
Dampening the Fire: A Negative Feedback Loop in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 Feb;64(2):158-160. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0487ED. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33522886 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Villar J, Blanco J, Kacmarek RM. Current incidence and outcome of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2016;22:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Millar FR, Summers C, Griffiths MJ, Toshner MR, Proudfoot AG. The pulmonary endothelium in acute respiratory distress syndrome: insights and therapeutic opportunities. Thorax. 2016;71:462–473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

