Impact of Long-Term HFD Intake on the Peripheral and Central IGF System in Male and Female Mice
- PMID: 33202914
- PMCID: PMC7698111
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo10110462
Impact of Long-Term HFD Intake on the Peripheral and Central IGF System in Male and Female Mice
Abstract
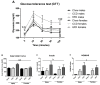
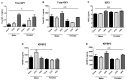
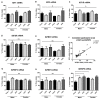
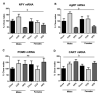
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system is responsible for growth, but also affects metabolism and brain function throughout life. New IGF family members (i.e., pappalysins and stanniocalcins) control the availability/activity of IGFs and are implicated in growth. However, how diet and obesity modify this system has been poorly studied. We explored how intake of a high-fat diet (HFD) or commercial control diet (CCD) affects the IGF system in the circulation, visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and hypothalamus. Male and female C57/BL6J mice received HFD (60% fat, 5.1 kcal/g), CCD (10% fat, 3.7 kcal/g) or chow (3.1 % fat, 3.4 kcal/g) for 8 weeks. After 7 weeks of HFD intake, males had decreased glucose tolerance (p < 0.01) and at sacrifice increased plasma insulin (p < 0.05) and leptin (p < 0.01). Circulating free IGF1 (p < 0.001), total IGF1 (p < 0.001), IGF2 (p < 0.05) and IGFBP3 (p < 0.01) were higher after HFD in both sexes, with CCD increasing IGFBP2 in males (p < 0.001). In VAT, HFD reduced mRNA levels of IGF2 (p < 0.05), PAPP-A (p < 0.001) and stanniocalcin (STC)-1 (p < 0.001) in males. HFD increased hypothalamic IGF1 (p < 0.01), IGF2 (p < 0.05) and IGFBP5 (p < 0.01) mRNA levels, with these changes more apparent in females. Our results show that diet-induced changes in the IGF system are tissue-, sex- and diet-dependent.
Keywords: IGF1; IGF2; IGFBP2; high-fat diet; neuropeptides; obesity; sex differences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sex Differences in Metabolic Recuperation After Weight Loss in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 16;12:796661. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.796661. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34975768 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Diet Induced Changes in the Central and Circulating IGF Systems Are Sex Specific.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Aug 11;11:513. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00513. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32849298 Free PMC article.
-
The metabolic effects of resumption of a high fat diet after weight loss are sex dependent in mice.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 14;13(1):13227. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40514-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37580448 Free PMC article.
-
Compared to casein, bovine lactoferrin reduces plasma leptin and corticosterone and affects hypothalamic gene expression without altering weight gain or fat mass in high fat diet fed C57/BL6J mice.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015 Dec 8;12:53. doi: 10.1186/s12986-015-0049-7. eCollection 2015. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26649066 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine serum albumin as the dominant form of dietary protein reduces subcutaneous fat mass, plasma leptin and plasma corticosterone in high fat-fed C57/BL6J mice.Br J Nutr. 2015 Aug 28;114(4):654-62. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515002123. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Br J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26189974
Cited by
-
Sex-based differences in growth-related IGF1 signaling in response to PAPP-A2 deficiency: comparative effects of rhGH, rhIGF1 and rhPAPP-A2 treatments.Biol Sex Differ. 2024 Apr 8;15(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00603-5. Biol Sex Differ. 2024. PMID: 38589872 Free PMC article.
-
IGF1 Signaling Regulates Neuropeptide Expression in Hypothalamic Neurons Under Physiological and Pathological Conditions.Endocrinology. 2025 Mar 24;166(5):bqaf051. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaf051. Endocrinology. 2025. PMID: 40105689 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in Metabolic Recuperation After Weight Loss in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 16;12:796661. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.796661. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34975768 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Behavioral Weight Loss and Metformin on IGFs in Cancer Survivors: A Randomized Trial.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Sep 27;106(10):e4179-e4191. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab266. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33884414 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Identification of hub genes and infiltrating immune cells in skeletal muscle in obesity.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Oct;10(19):1052. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-1010. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36330393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lui J.C., Finkielstain G.P., Barnes K.M., Baron J. An imprinted gene network that controls mammalian somatic growth is down-regulated during postnatal growth deceleration in multiple organs. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008;295:R189–R196. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00182.2008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

