Co-Administration of Drugs and Parenteral Nutrition: In Vitro Compatibility Studies of Loop Diuretics for Safer Clinical Practice
- PMID: 33202945
- PMCID: PMC7696202
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12111092
Co-Administration of Drugs and Parenteral Nutrition: In Vitro Compatibility Studies of Loop Diuretics for Safer Clinical Practice
Abstract
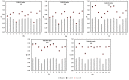
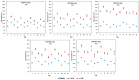
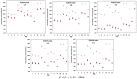
Parenteral nutrition (PN) admixtures are prone to interacting with drugs administered intravenously via a common catheter. This may cause a threat to a patient's health and life. The literature that has been reported on the compatibility of loop diuretics with PN presents conflicting results. This work aimed to study the compatibility of furosemide and torsemide with PN used in clinical practice. Undiluted solutions of drugs were mixed with PN at various ratios determined by flow rates. In order to assess compatibility, visual control was followed by pH measurement, osmolality, mean emulsion droplet diameter (MDD), and zeta potential upon mixing and at 4 h of storage. No macroscopic changes that indicated lipid emulsion degradation were observed. After the addition of the drugs, the value of pH ranged from 6.37 ± 0.01 to 7.38 ± 0.01. The zeta potential was in reverse proportion to the drug concentration. The addition of the drugs did not affect the MDD. It may be suggested that the co-administration of furosemide or torsemide and PN caused no interaction. The absence of such signs of unwanted interactions allowed for the co-administration of the mentioned loop diuretics and PN at each of the studied ratios.
Keywords: Y-site administration; compatibility; drug interactions; loop diuretics; parenteral nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

