Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Supplementation in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review of Human Studies
- PMID: 33202952
- PMCID: PMC7696060
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9111128
Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Supplementation in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review of Human Studies
Abstract
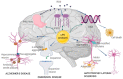
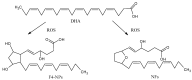
Being characterized by progressive and severe damage in neuronal cells, neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) are the major cause of disability and morbidity in the elderly, imposing a significant economic and social burden. As major components of the central nervous system, lipids play important roles in neural health and pathology. Disturbed lipid metabolism, particularly lipid peroxidation (LPO), is associated with the development of many NDDs, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), all of which show elevated levels of LPO products and LPO-modified proteins. Thus, the inhibition of neuronal oxidation might slow the progression and reduce the severity of NDD; natural antioxidants, such as polyphenols and antioxidant vitamins, seem to be the most promising agents. Here, we summarize current literature data that were derived from human studies on the effect of natural polyphenols and vitamins A, C, and E supplementation in patients with AD, PD, and ALS. Although these compounds may reduce the severity and slow the progression of NDD, research gaps remain in antioxidants supplementation in AD, PD, and ALS patients, which indicates that further human studies applying antioxidant supplementation in different forms of NDDs are urgently needed.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; antioxidant supplementation; lipid peroxidation; neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Desikan R.S., Fan C.C., Wang Y., Schork A.J., Cabral H.J., Cupples L.A., Thompson W.K., Besser L., Kukull W.A., Holland D., et al. Genetic assessment of age-associated Alzheimer disease risk: Development and validation of a polygenic hazard score. PLoS Med. 2017;14:e1002258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002258. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gandhi J., Antonelli A.C., Afridi A., Vatsia S., Joshi G., Romanov V., Murray I.V.J., Khan S.A. Protein misfolding and aggregation in neurodegenerative diseases: A review of pathogeneses, novel detection strategies, and potential therapeutics. Rev. Neurosci. 2019;30:339–358. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2016-0035. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

