Assessment of a Novel Adult Mass-Rearing Cage for Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Anopheles arabiensis (Patton)
- PMID: 33202973
- PMCID: PMC7697024
- DOI: 10.3390/insects11110801
Assessment of a Novel Adult Mass-Rearing Cage for Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Anopheles arabiensis (Patton)
Abstract
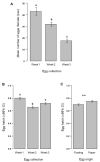
Successful implementation of the sterile insect technique (SIT) against Aedes albopictus and Anopheles arabiensis relies on a continuous supply of sterile males. To meet this requirement, optimization of the mass-rearing techniques is needed. This study, therefore, aims to assess a new mass-rearing cage (MRC) in terms of egg production efficiency and egg hatch rate (quality). In addition, adult survival was evaluated based on a cage adult-index for Ae. albopictus. Moreover, the cage's suitability for use in mass An. arabiensis egg production was compared to that of the FAO/IAEA Anopheles reference cage. In Ae. albopictus rearing, the new MRC produced 1,112,110 eggs per cage following six blood meals, with minimum loss of eggs in the egging water. Furthermore, the adult index gave a good proxy of daily mortality rates in Ae. albopictus. In An. arabiensis rearing, about 130,000 eggs per egg batch were collected both from the new and the reference MRC. These findings suggest that the new MRC prototype is efficient in terms of egg production and can be used for mass-rearing in SIT programs targeting Ae. albopictus as well as An. arabiensis. The adult index was also positively validated for the detection of unusual mortality rates in Ae. albopictus mass-rearing facilities. Overall, the new MRC has shown several advantages; however, further improvements are necessary to minimize escapes during the egg collection processes.
Keywords: adult index; dengue; egg production; genetic control; insect cage; malaria; plexiglass; sterile insect technique.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hawley W.A. The biology of Aedes albopictus. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. Suppl. 1988;1:1–39. - PubMed
-
- World-Malaria-Report-2019. [(accessed on 18 June 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail/world-malaria-report-2019.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

