The Impact of Surfactant Composition and Surface Charge of Niosomes on the Oral Absorption of Repaglinide as a BCS II Model Drug
- PMID: 33204087
- PMCID: PMC7667196
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S261932
The Impact of Surfactant Composition and Surface Charge of Niosomes on the Oral Absorption of Repaglinide as a BCS II Model Drug
Abstract
Background: Niosomes, bilayer vesicles formed by the self-assembly of nonionic surfactants, are receiving increasing attention as potential oral drug delivery systems but the impact of niosomal formulation parameters on their oral capability has not been studied systematically. The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of surfactant composition and surface charge of niosomes in enhancing oral bioavailability of repaglinide (REG) as a BCS II model drug.
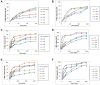
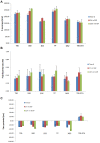
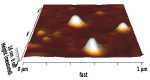
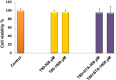
Methods: Niosomes (13 formulations) from various nonionic surfactants having HLB in the range of 4-28 (Tweens, Spans, Brijs, Myrj, poloxamer 188, TPGS and Labrasol) were prepared and characterized concerning their loading efficiency, hydrodynamic diameter, zeta potential, drug release profile, and stability. The oral pharmacokinetics of the selected formulations were studied in rats (8 in vivo groups).
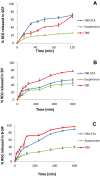
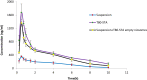
Results: The results revealed that type of surfactant markedly affected the in vitro and in vivo potentials of niosomes. The Cmax and AUC values of REG after administration of the selected niosomes as well as the drug suspension (as control) were in the order of Tween 80> TPGS> Myrj 52> Brij 35> Span 60≈Suspension. Adding stearyl amine as a positive charge-inducing agent to the Tween 80-based niosomes, resulted in an additional increase in drug absorption and values of AUC and Cmax were 3.8- and 4.7-fold higher than the drug suspension, respectively.
Conclusion: Cationic Tween 80-based niosomes may represent a promising platform to develop oral delivery systems for BCS II drugs.
Keywords: BCS II; HLB; niosome; oral bioavailability; repaglinide; surface charge; surfactant type.
© 2020 Yaghoobian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Darwich AS, Neuhoff S, Jamei M, Rostami-Hodjegan A. Interplay of metabolism and transport in determining oral drug absorption and gut wall metabolism: a simulation assessment using the “Advanced Dissolution, Absorption, Metabolism (ADAM)” model. Curr Drug Metab. 2010;11(9):716–729. doi: 10.2174/138920010794328913 - DOI - PubMed
-
- McClements DJ. Nanoemulsion-based oral delivery systems for lipophilic bioactive components: nutraceuticals and pharmaceuticals. Ther Deliv. 2013;4(7):841–857. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

