Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of Syzygium nervosum
- PMID: 33204293
- PMCID: PMC7652606
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8263670
Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of Syzygium nervosum
Abstract
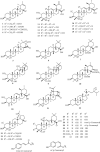
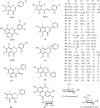
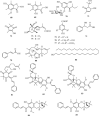
Syzygium nervosum, which belongs to the Myrtaceae plant family, is widely distributed and cultivated in South East Asian countries. The decoction of S. nervosum leaves and flower buds has been consumed regularly as a beverage among the Vietnamese and Chinese communities. In addition, it has also been used in traditional medicine for a variety of purposes, notably for influenza, skin diseases, and digestive conditions. To date, there has been a considerable number of publications on chemical profiling and pharmacological activities of S. nervosum crude extract and pure isolated compounds. Our analysis indicated the characteristic chemical scaffolds and potential bioactivities on cancer, diabetes, and inflammatory diseases of this plant. The review aims to summarize up-to-date past study results and suggest future research direction on this species, in order to promote clinical applications of S. nervosum.
Copyright © 2020 Giang Nam Pham et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Do T. L. Vietnamese Medicinal Plants and Herbs. 12th. Hanoi, Vietnam: Medical Publishing House; 2004.
-
- Nanjing China Medical University. Dictionary of Chinese Medicine. Shanghai, China: Shanghai Science Publishing House; 2005.
-
- National Institute of Medicinal Materials. Medicinal Plants and Animals in Vietnam-Volume 2. Shanghai, China: Science and Technology Publishing House; 2006.
-
- Vietnam Pharmacopoeia Council. Vietnam Pharmacopoeia V. Hanoi, Vietnam: Medical Publishing House; 2017.
-
- Editorial Committee of Guangdong Chinese Medicine Journal. Guangdong Chinese Medicine Journal. Guangdong, China: Guangdong Science and Technology Press; 1994.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous