Anti-Inflammatory Diets and Schizophrenia
- PMID: 33204665
- PMCID: PMC7644368
- DOI: 10.7762/cnr.2020.9.4.241
Anti-Inflammatory Diets and Schizophrenia
Abstract
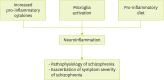
Schizophrenia is a mental illness characterized by symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech, disorganized or catatonic behavior, and negative symptoms (emotional flatness, apathy, and lack of speech). It causes social and economic burdens to patients and their family. Although etiology of schizophrenia is still uncertain, dopamine dysregulation is traditionally considered as a main etiological factor of schizophrenia, which has been utilized to develop drugs for treating schizophrenia. Recently, inflammation has presented being a risk factor for schizophrenia in that neuroinflammation contributes to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and the exacerbation of symptom severity. Various factors including diet can regulate inflammatory state. Specific foods or dietary patterns have anti- or pro-inflammatory potentials. Increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and microglia activation have been reported in schizophrenia populations and were related to the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Omega-3 fatty acids were often recommended to schizophrenia patients because of their anti-inflammatory activities. In this review, we investigate the inflammation-related pathogenesis of schizophrenia and summarize potential nutritional approaches to inhibit the manifestation of symptoms and to alleviate symptom severity using anti-inflammatory nutrients or functional components.
Keywords: Cytokines; Inflammation; Microglia; Omega-3 fatty acids.
Copyright © 2020. The Korean Society of Clinical Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources