Pharmacogenomics of genetic polymorphism within the genes responsible for SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility and the drug-metabolising genes used in treatment
- PMID: 33205496
- PMCID: PMC7744885
- DOI: 10.1002/rmv.2194
Pharmacogenomics of genetic polymorphism within the genes responsible for SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility and the drug-metabolising genes used in treatment
Abstract
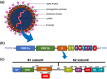
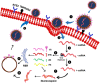
The ongoing outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) represents a significant challenge to international health. Pharmacogenomics aims to identify the different genetic variations that exist between individuals and populations in order to determine appropriate treatment protocols to enhance the efficacy of drugs and reduce their side-effects. This literature review provides an overview of recent studies of genetic polymorphisms in genes that mediate the SARS-CoV-2 infection mechanism (ACE1, ACE2, TMPRSS2 and CD26). In addition, genetic variations in the drug-metabolising enzyme genes of several selected drugs used in the treatment of COVID-19 are summarised. This may help construct an effective health protocol based on genetic biomarkers to optimise response to treatment. Potentially, pharmacogenomics could contribute to the development of effective high-throughput assays to improve patient evaluation, but their use will also create ethical, medical, regulatory, and legal issues, which should now be considered in the era of personalised medicine.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; drug metabolising genes; pharmacogenomics; susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2020. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

