The receptor tyrosine kinase torso regulates ecdysone homeostasis to control developmental timing in Bombyx mori
- PMID: 33205532
- PMCID: PMC9291747
- DOI: 10.1111/1744-7917.12879
The receptor tyrosine kinase torso regulates ecdysone homeostasis to control developmental timing in Bombyx mori
Abstract
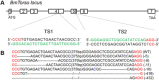
Insect growth and development are precisely controlled by hormone homeostasis. The prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) receptor, Torso, is a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase family in insects. Activation of Torso by PTTH triggers biosynthesis and release of the steroid hormone in the prothoracic gland (PG). Although numbers of genes functioning in steroid hormone synthesis and metabolism have been identified in insects, the PTTH transduction pathway via its receptor Torso is poorly understood. In the current study, we describe a loss-of-function analysis of Torso in the silkworm, Bombyx mori, by targeted gene disruption using the transgenic CRISPR/Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases) system. Depletion of B. mori Torso (BmTorso) did not eventually affect larval ecdysis and metamorphosis processes. Instead, BmTorso deficiency resulted in significant extension of developing time during larval and pupal stages with increased pupa and cocoon sizes. The ecdysteriod titers in the hemolymph of BmTorso mutants sharpy declined. Transcriptional levels of genes involved in ecdysone biosynthesis and ecdysteroid signaling pathways were significantly reduced in BmTorso-deficient animals. Additionally, RNA-Seq analysis revealed that genes involved in the longevity pathway and protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum pathway were affected after BmTorso deletion. These results indicate that Torso is critical for maintaining steroid hormone homeostasis in insects.
Keywords: Bombyx mori; CRISPR/Cas9; Torso; developmental timing.
© 2020 The Authors. Insect Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Figures



References
-
- Colombani, J. , Bianchini, L. , Layalle, S. , Pondeville, E. , Dauphin‐Villemant, C. , Antoniewski, C. et al. (2005) Antagonistic actions of ecdysone and longevitys determine final size in Drosophila . Science, 310, 667–670. - PubMed
-
- Cruz, J. , Martín, D. and Franch‐Marro, X. (2020) Egfr signaling is a major regulator of ecdysone biosynthesis in the Drosophila prothoracic gland. Current Biology, 30, 1547–1554. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert, L.I. (2004) Halloween genes encode P450 enzymes that mediate steroid hormone biosynthesis in Drosophila melanogaster . Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 215, 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert, L.I. , Rybczynski, R. and Warren, J.T. (2002) Control and biochemical nature of the ecdysteroidogenic pathway. Annual Review of Entomology, 47, 883–916. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

