Missense mutations in EDA and EDAR genes cause dominant syndromic tooth agenesis
- PMID: 33205897
- PMCID: PMC7963410
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.1555
Missense mutations in EDA and EDAR genes cause dominant syndromic tooth agenesis
Abstract
Background: Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (HED) is the most common form of ectodermal dysplasia and is mainly associated with mutations in the EDA, EDAR, and EDARADD responsible for the development of ectodermal-derived structures. HED displays different modes of inheritance according to the gene that is involved, with X-linked EDA-related HED being the most frequent form of the disease.
Methods: Two families with tooth agenesis and manifestations of HED underwent clinical examination and EDA, EDAR, and EDARADD genetic analysis. The impact of the novel variant on the protein was evaluated through bioinformatics tools, whereas molecular modeling was used to predict the effect on the protein structure.
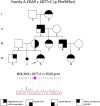
Results: A novel missense variant was identified in the EDAR (c.287T>C, p.Phe96Ser) of a female child proband and her mother, accounting for autosomal dominant HED. The genetic variant c.866G>A (p.Arg289His) in EDA, which has been previously described, was observed in the male proband of another family confirming its role in X-linked HED. The inheritance model of the missense mutation showed a different relationship with X-linked HED and non-syndromic tooth agenesis.
Conclusion: Our findings provide evidence of variable expression of HED in heterozygous females, which should be considered for genetic counseling, and different modes of inheritance related to tooth development.
Keywords: EDA; EDAR; ectodermal dysplasia; hypodontia.
© 2020 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bashyam, M. D. , Chaudhary, A. K. , Reddy, E. C. , Reddy, V. , Acharya, V. , Nagarajaram, H. A. , Devi, A. , Bashyam, L. , Dalal, A. B. , Gupta, N. , Kabra, M. , Agarwal, M. , Phadke, S. R. , Tainwala, R. , Kumar, R. , & Hariharan, S. V. (2012). A founder ectodysplasin A receptor (EDAR) mutation results in a high frequency of the autosomal recessive form of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in India. British Journal of Dermatology, 166(4), 819–829. 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10707.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary, A. K. , Mohapatra, R. , Nagarajaram, H. A. , Ranganath, P. , Dalal, A. , Dutta, A. , & Bashyam, M. D. (2017). The novel EDAR p. L397H missense mutation causes autosomal dominant hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 31(1), e17–e20. 10.1111/jdv.13587 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cluzeau, C. , Hadj‐Rabia, S. , Jambou, M. , Mansour, S. , Guigue, P. , Masmoudi, S. , Bal, E. , Chassaing, N. , Vincent, M.‐C. , Viot, G. , Clauss, F. , Manière, M.‐C. , Toupenay, S. , Le Merrer, M. , Lyonnet, S. , Cormier‐Daire, V. , Amiel, J. , Faivre, L. , de Prost, Y. , … Smahi, A. (2011). Only four genes (EDA1, EDAR, EDARADD, and WNT10A) account for 90% of hypohidrotic/anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia cases. Human Mutation, 32(1), 70–72. 10.1002/humu.21384 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

