Evaluation of the IR Biotyper for Klebsiella pneumoniae typing and its potentials in hospital hygiene management
- PMID: 33205912
- PMCID: PMC8313285
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13709
Evaluation of the IR Biotyper for Klebsiella pneumoniae typing and its potentials in hospital hygiene management
Abstract
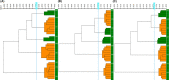
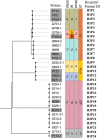
Klebsiella pneumoniae has emerged as one of the most important pathogens that frequently encounter in community-acquired or hospital-acquired infections. Timely epidemiological surveillance could greatly facilitate infection control of K. pneumoniae and many deadly pathogens alike. In this study, we evaluated the performance of the IR Biotyper, a Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy system for K. pneumoniae isolates typing through (i) optimizing the culture scheme and defining the cutoff value (COV) range and (ii) comparing with commonly used typing tools such as multi-locus sequence typing (MLST), pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS). We found that a non-selective and non-chromogenic medium with 24 ± 2 h incubation gives the best discriminatory power for the IR Biotyper (IRBT). COV evaluation indicated that the IRBT is a robust typing method with good reproducibility. Besides, we observed that the modified H2 O-EtOH suspensions preparation method could enhance the quality of the spectrum, especially for those hypermucoviscous strains. For the method comparison study, our data demonstrated that FTIR spectroscopy could accurately cluster K. pneumoniae strains. The typing results of the IRBT were almost entirely in concordance with those from PFGE and WGS. Together with the advantages such as low costs and short turnaround time (less than 3h), the IRBT is a promising tool for strain typing that could make real-time outbreak investigation a reality.
© 2020 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Applied Microbiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of IR Biotyper for carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa typing and its application potential for the investigation of nosocomial infection.Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 9;14:1068872. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1068872. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36846786 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of IR Biotyper for Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Typing and Its Application Potential in Probiotic Preliminary Screening.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 24;13:823120. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.823120. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35401469 Free PMC article.
-
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Is a New Option for Outbreak Investigation: a Retrospective Analysis of an Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Outbreak in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Apr 23;58(5):e00098-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00098-20. Print 2020 Apr 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32161093 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter evaluation of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy as a first-line typing tool for carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in clinical settings.J Clin Microbiol. 2025 Jan 31;63(1):e0112224. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01122-24. Epub 2024 Nov 27. J Clin Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39601577 Free PMC article.
-
The IR Biotyper as a tool for typing organisms of significance for hospital epidemiology- A subject review.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025 Mar;111(3):116676. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2024.116676. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39756141 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular typing methods & resistance mechanisms of MDR Klebsiella pneumoniae.AIMS Microbiol. 2023 Feb 27;9(1):112-130. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2023008. eCollection 2023. AIMS Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36891535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy as a new tool for surveillance in local stewardship antimicrobial program: a retrospective study in a nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii outbreak.Braz J Microbiol. 2022 Sep;53(3):1349-1353. doi: 10.1007/s42770-022-00774-6. Epub 2022 May 30. Braz J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35644906 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiology and molecular typing methods of Acinetobacter baumannii: An updated review.Saudi Med J. 2024 May;45(5):458-467. doi: 10.15537/smj.2024.45.5.20230886. Saudi Med J. 2024. PMID: 38734425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classification of Salmonella enterica of the (Para-)Typhoid Fever Group by Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy.Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 15;9(4):853. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040853. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33921159 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Colistin Resistance: An Antibiotic of Last Resort.Microorganisms. 2024 Apr 11;12(4):772. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040772. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674716 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Campos, J. , Sousa, C. , Mourao, J. , Lopes, J. , Antunes, P. , and Peixe, L. (2018) Discrimination of non‐typhoid salmonella serogroups and serotypes by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: a comprehensive analysis. Int J Food Microbiol 285: 34–41. - PubMed
-
- Carrico, J.A. , Silva‐Costa, C. , Melo‐Cristino, J. , Pinto, F. R. , de Lencastre, H. , Almeida, J.S. , and Ramirez, M. (2006) Illustration of a common framework for relating multiple typing methods by application to macrolide‐resistant Streptococcus pyogenes. J Clin Microbiol 44: 2524–2532. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Enright, M.C. , and Spratt, B.G. (1999) Multilocus sequence typing. Trends Microbiol 7: 482–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

