Targeted and untargeted quantification of quorum sensing signalling molecules in bacterial cultures and biological samples via HPLC-TQ MS techniques
- PMID: 33206214
- PMCID: PMC7809007
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-020-03040-6
Targeted and untargeted quantification of quorum sensing signalling molecules in bacterial cultures and biological samples via HPLC-TQ MS techniques
Abstract
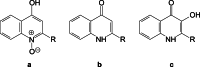
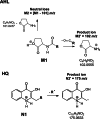
Quorum sensing (QS) is the ability of some bacteria to detect and to respond to population density through signalling molecules. QS molecules are involved in motility and cell aggregation mechanisms in diseases such as sepsis. Few biomarkers are currently available to diagnose sepsis, especially in high-risk conditions. The aim of this study was the development of new analytical methods based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for the detection and quantification of QS signalling molecules, including N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHL) and hydroxyquinolones (HQ), in biofluids. Biological samples used in the study were Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterial cultures and plasma from patients with sepsis. We developed two MS analytical methods, based on neutral loss (NL) and product ion (PI) experiments, to identify and characterize unknown AHL and HQ molecules. We then established a multiple-reaction-monitoring (MRM) method to quantify specific QS compounds. We validated the HPLC-MS-based approaches (MRM-NL-PI), and data were in accord with the validation guidelines. With the NL and PI MS-based methods, we identified and characterized 3 and 13 unknown AHL and HQ compounds, respectively, in biological samples. One of the newly found AHL molecules was C12-AHL, first quantified in Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterial cultures. The MRM quantitation of analytes in plasma from patients with sepsis confirmed the analytical ability of MRM for the quantification of virulence factors during sepsis. Graphical abstract.
Keywords: Homoserine lactones; Hydroxyquinolones; Mass spectrometry; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Quorum sensing molecules; Triple quadrupole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

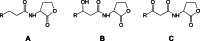

References
-
- Rajeshkannan E, Saini S. Physiological advantage of phenotypic heterogeneity in a quorum-sensing population. J Indian Inst Sci. 2020; 100:485–96. 10.1007/s41745-020-00175-4.
-
- Leichnitz D, Raguž L, Beemelmanns C. Total synthesis and functional analysis of microbial signaling molecules. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(20):6330–6344. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

