Atypical UV Photoproducts Induce Non-canonical Mutation Classes Associated with Driver Mutations in Melanoma
- PMID: 33207206
- PMCID: PMC7709870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108401
Atypical UV Photoproducts Induce Non-canonical Mutation Classes Associated with Driver Mutations in Melanoma
Abstract
Somatic mutations in skin cancers and other ultraviolet (UV)-exposed cells are typified by C>T and CC>TT substitutions at dipyrimidine sequences; however, many oncogenic "driver" mutations in melanoma do not fit this UV signature. Here, we use genome sequencing to characterize mutations in yeast repeatedly irradiated with UV light. Analysis of ~50,000 UV-induced mutations reveals abundant non-canonical mutations, including T>C, T>A, and AC>TT substitutions. These mutations display transcriptional asymmetry that is modulated by nucleotide excision repair (NER), indicating that they are caused by UV photoproducts. Using a sequencing method called UV DNA endonuclease sequencing (UVDE-seq), we confirm the existence of an atypical thymine-adenine photoproduct likely responsible for UV-induced T>A substitutions. Similar non-canonical mutations are present in skin cancers, which also display transcriptional asymmetry and dependence on NER. These include multiple driver mutations, most prominently the recurrent BRAF V600E and V600K substitutions, suggesting that mutations arising from rare, atypical UV photoproducts may play a role in melanomagenesis.
Keywords: BRAF; NRAS; UV damage; UV mutagenesis; skin cancer; thymine-adenine photoproduct; transcriptional asymmetry.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



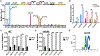



References
-
- Besaratinia A, Yoon JI, Schroeder C, Bradforth SE, Cockburn M, and Pfeifer GP (2011). Wavelength dependence of ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage as determined by laser irradiation suggests that cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers are the principal DNA lesions produced by terrestrial sunlight. FASEB J. 25, 3079–3091. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bose SN, Davies RJ, Sethi SK, and McCloskey JA (1983). Formation of an adenine-thymine photoadduct in the deoxydinucleoside monophosphate d(TpA) and in DNA. Science 220, 723–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

