Recovery of a Bacteriocin-Like Inhibitory Substance from Lactobacillus bulgaricus FTDC 1211 Using Polyethylene-Glycol Impregnated Amberlite XAD-4 Resins System
- PMID: 33207534
- PMCID: PMC7697619
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25225332
Recovery of a Bacteriocin-Like Inhibitory Substance from Lactobacillus bulgaricus FTDC 1211 Using Polyethylene-Glycol Impregnated Amberlite XAD-4 Resins System
Abstract
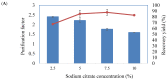
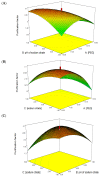
Lactobacillus bulgaricus is a LAB strain which is capable of producing bacteriocin substances to inhibit Staphylococcus aureus. The aim of this study was to purify a bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance (BLIS) produced by L. bulgaricus FTDC 1211 using an aqueous impregnated resins system consisting of polyethylene-glycol (PEG) impregnated on Amberlite XAD4. Important parameters influencing on purification of BLIS, such as the molecular weight and concentration of PEG, the concentration and pH of sodium citrate and the concentration of sodium chloride, were optimized using a response surface methodology. Under optimum conditions of 11% (w/w) of PEG 4000 impregnated Amberlite XAD4 resins and 2% (w/w) of sodium citrate at pH 6, the maximum purification factor (3.26) and recovery yield (82.69% ± 0.06) were obtained. These results demonstrate that AIRS could be used as an alternate purification system in the primary recovery step.
Keywords: bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance; lactic acid bacteria; polymer; purification; resin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abbasiliasi S., Tan J.S., Ibrahim T.A.T., Ramanan R.N., Vakhshiteh F., Mustafa S., Ling T.C., Rahim R.A., Ariff A.B. Isolation of Pediococcus acidilactici Kp10 with ability to secrete bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance from milk products for applications in food industry. BMC Microbiol. 2012;12:260. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-260. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hor Y.Y., Liong M.T. Use of extracellular extracts of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria for the inhibition of dermatological pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. Dermatol. Sin. 2014;32:141–147. doi: 10.1016/j.dsi.2014.03.001. - DOI
-
- Abbasiliasi S., Tan J.S., Ibrahim T.A.T., Kadkhodaei S., Ng H.S., Vakhshiteh F., Ajdari Z., Mustafa S., Ling T.C., Rahim R.A. Primary recovery of a bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance derived from Pediococcus acidilactici Kp10 by an aqueous two-phase system. Food Chem. 2014;151:93–100. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.11.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang J., Yang Y., Yang H., Bu Y., Yi H., Zhang L., Han X., Ai L. Purification and partial characterization of Bacteriocin Lac-B23, a novel Bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus plantarum J23, isolated from Chinese traditional fermented milk. Front. Microbiol. 2018;9:2165. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02165. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

