Safety and Tolerability of SRX246, a Vasopressin 1a Antagonist, in Irritable Huntington's Disease Patients-A Randomized Phase 2 Clinical Trial
- PMID: 33207828
- PMCID: PMC7696926
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9113682
Safety and Tolerability of SRX246, a Vasopressin 1a Antagonist, in Irritable Huntington's Disease Patients-A Randomized Phase 2 Clinical Trial
Abstract
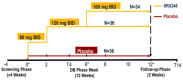
SRX246 is a vasopressin (AVP) 1a receptor antagonist that crosses the blood-brain barrier. It reduced impulsive aggression, fear, depression and anxiety in animal models, blocked the actions of intranasal AVP on aggression/fear circuits in an experimental medicine fMRI study and demonstrated excellent safety in Phase 1 multiple-ascending dose clinical trials. The present study was a 3-arm, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, 12-week, dose escalation study of SRX246 in early symptomatic Huntington's disease (HD) patients with irritability. Our goal was to determine whether SRX246 was safe and well tolerated in these HD patients given its potential use for the treatment of problematic neuropsychiatric symptoms. Participants were randomized to receive placebo or to escalate to 120 mg twice daily or 160 mg twice daily doses of SRX246. Assessments included standard safety tests, the Unified Huntington's Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS), and exploratory measures of problem behaviors. The groups had comparable demographics, features of HD and baseline irritability. Eighty-two out of 106 subjects randomized completed the trial on their assigned dose of drug. One-sided exact-method confidence interval tests were used to reject the null hypothesis of inferior tolerability or safety for each dose group vs. placebo. Apathy and suicidality were not affected by SRX246. Most adverse events in the active arms were considered unlikely to be related to SRX246. The compound was safe and well tolerated in HD patients and can be moved forward as a candidate to treat irritability and aggression.
Keywords: Huntington’s disease; safety; tolerability; vasopressin 1a receptor antagonist.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding: National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke SBIR Fast-track award to Azevan Pharmaceuticals, Inc (U44NS090616), NINDS grants supporting the NeuroNext Network (Clinical Coordinating Center U01NS077179; Data Coordinating Center U01NS077352), the CHDI Foundation (grant to NGS) and Azevan Pharmaceuticals, Inc. The STAIR trial was sponsored by Azevan Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and was conducted through the NINDS NeuroNEXT Network (22 sites).
Figures
References
-
- FDA The Voice of the Patient: Huntington’s Disease. 2016 Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/96196.
-
- Fabio K., Guillon C., Lu S., Heindel N., Miller M., Ferris C., Brownstein M.J., Garripa C., Steiner M., Coccaro E., et al. Vasopressin antagonists as anxiolytics and antidepressants: Recent developments. Front. CNS Drug Discov. 2010;1:156–183. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

