The Association between Drinking Water Quality and Inflammatory Bowel Disease-A Study in Eastern Croatia
- PMID: 33207850
- PMCID: PMC7697303
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17228495
The Association between Drinking Water Quality and Inflammatory Bowel Disease-A Study in Eastern Croatia
Abstract
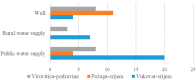
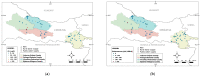
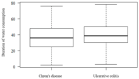
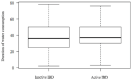
The incidence rate of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is becoming a global health problem that could be caused by changes in environmental and lifestyle habits. The study aimed to identify the association between the quality of drinking water, i.e., physiochemical and biological aspects of the phenotype and activity of IBD in Eastern Croatia. The study included 312 patients (63.4% ulcerative colitis, UC, and 36.6% Crohn's disease, CD) from the area of Eastern Croatia. The data were collected by questionnaires and the analysis of the water safety, based on 65 samples of drinking water by the patient's water supply method (public supply, rural water supply, and private well). IBD was active in 38.0% patients (34.0% CD and 40.0% UC). Significant differences (p = 0.001) were observed in the distribution of patients, according to counties in which they lived in. The largest deviation was noted in coliform bacteria, Escherichia coli, and enterococci bacteria, Fe, Al, and nitrate in rural water supply and private wells, although, without significant impact on IBD phenotype and activity. The hazard quotient (HQ) simulations showed that children are a sensitive group, regarding exposure to nitrates in drinking water over a long period of time, so there is a need for further monitoring and analysis of this issue.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; Eastern Croatia; drinking water quality; inflammatory bowel disease; private wells; rural public supply; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A retrospective, case-control study on traditional environmental risk factors in inflammatory bowel disease in Vukovar-Srijem County, north-eastern Croatia, 2010.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2015 May;127(9-10):345-54. doi: 10.1007/s00508-015-0741-7. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2015. PMID: 25821054
-
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Occurrence, course and prognosis during the first year of disease in a European population-based inception cohort.Dan Med J. 2014 Jan;61(1):B4778. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 24393595
-
A four-decade analysis of the incidence trends, sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of inflammatory bowel disease patients at single tertiary centre, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.BMC Public Health. 2019 Jun 13;19(Suppl 4):550. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-6858-2. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31196184 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiating ulcerative colitis from Crohn disease in children and young adults: report of a working group of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007 May;44(5):653-74. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31805563f3. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17460505
-
Familial occurrence and inheritance studies in inflammatory bowel disease.Neth J Med. 1996 Feb;48(2):53-6. doi: 10.1016/0300-2977(95)00093-3. Neth J Med. 1996. PMID: 8819799 Review.
References
-
- Burisch J. Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Occurrence, course and prognosis during the first year of disease in a European population-based inception cohort. Dan. Med. J. 2014;61:B4778. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

