Endothelialitis plays a central role in the pathophysiology of severe COVID-19 and its cardiovascular complications
- PMID: 33208052
- PMCID: PMC7682384
- DOI: 10.1080/00015385.2020.1846921
Endothelialitis plays a central role in the pathophysiology of severe COVID-19 and its cardiovascular complications
Abstract
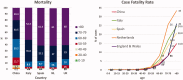
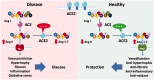
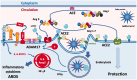
This clinical review paper discusses the pathophysiology of the pulmonary and cardiovascular manifestations of a SARS-CoV-2 infection and the ensuing implications on acute cardiovascular care in patients presenting with a severe COVID-19 syndrome admitted to an intensive acute cardiac care unit. The high prevalence of old age, obesity, diabetes, hypertension, heart failure, and ischaemic heart disease in patients who develop a severe to critical COVID-19 syndrome suggests shared pathophysiological mechanisms. Pre-existing endothelial dysfunction and an impaired innate immune response promote the development by the viral infection of an acute endothelialitis in the pulmonary microcirculation complicated by abnormal vasoconstrictor responses, luminal plugging by inflammatory cells, and intravascular thrombosis. This endothelialitis extends into the systemic circulation what may lead to acute myocardial injury, myocarditis, and thromboembolic complications both in the arterial and venous circulation.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; adult respiratory distress syndrome; cytokine storm; diabetes; endothelialitis; endothelium; microcirculation; obesity; thrombosis; ventilation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU) . COVID-19 Map - Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center; 2020. [2020 Jun 24]. Available from: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019. (COVID-19). 2020. Available from : https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/who-china-joint-mis....
-
- Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S.. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1775–1776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
