Cobomarsen, an Oligonucleotide Inhibitor of miR-155, Slows DLBCL Tumor Cell Growth In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 33208342
- PMCID: PMC8287597
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3139
Cobomarsen, an Oligonucleotide Inhibitor of miR-155, Slows DLBCL Tumor Cell Growth In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
Purpose: miRNA-155 is an oncogenic miRNA highly expressed in B-cell malignancies, particularly in the non-germinal center B-cell or activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (ABC-DLBCL), where it is considered a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. Thus, miR-155 inhibition represents an important therapeutic strategy for B-cell lymphomas. In this study, we tested the efficacy and pharmacodynamic activity of an oligonucleotide inhibitor of miR-155, cobomarsen, in ABC-DLBCL cell lines and in corresponding xenograft mouse models. In addition, we assessed the therapeutic efficacy and safety of cobomarsen in a patient diagnosed with aggressive ABC-DLBCL.
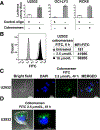
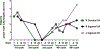
Experimental design: Preclinical studies included the delivery of cobomarsen to highly miR-155-expressing ABC-DLBCL cell lines to assess any phenotypic changes, as well as intravenous injections of cobomarsen in NSG mice carrying ABC-DLBCL xenografts, to study tumor growth and pharmacodynamics of the compound over time. To begin to test its safety and therapeutic efficacy, a patient was recruited who underwent five cycles of cobomarsen treatment.
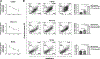
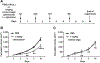
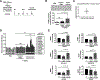
Results: Cobomarsen decreased cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in ABC-DLBCL cell lines. Intravenous administration of cobomarsen in a xenograft NSG mouse model of ABC-DLBCL reduced tumor volume, triggered apoptosis, and derepressed direct miR-155 target genes. Finally, the compound reduced and stabilized tumor growth without any toxic effects for the patient.
Conclusions: Our findings support the potential therapeutic application of cobomarsen in ABC-DLBCL and other types of lymphoma with elevated miR-155 expression.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
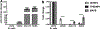
References
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000;403:503–11. - PubMed
-
- Li S, Young KH, Medeiros LJ. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Pathology 2018;50: 74–87. - PubMed
-
- Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P, et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 2007;109:1857–61. - PubMed
-
- Nowakowski GS, Czuczman MS. ABC, GCB, and double-hit diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: does subtype make a difference in therapy selection? Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 2015:e449–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

