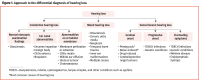
Approach to hearing loss
Abstract
Objective: To provide family physicians with a practical evidence-based approach to the management of patients with hearing loss.
Sources of information: MEDLINE and PubMed databases were searched for English-language hearing loss research, review articles, and guidelines published between 1980 and 2020. Most of the retrieved articles provided level II or III evidence.
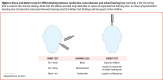
Main message: Hearing loss is one of the most common sensory impairments worldwide and causes great detriment to a patient's overall well-being by affecting physical health, finances, social inclusion, and mental health. A robust clinical assessment of hearing loss includes a history and physical examination that effectively characterizes the deficit as conductive, sensorineural, or mixed. Patients presenting with red flags (such as sudden unilateral sensorineural hearing loss) must be urgently referred to otolaryngology-head and neck surgery or immediately assessed in the emergency department. Many nonurgent presentations of hearing loss will also require referral for further audiological assessment, diagnosis, and management.
Conclusion: As primary care providers, family physicians are well equipped to manage the psychological concerns associated with hearing loss and to reinforce conservative treatment strategies. Frequently, referral or urgent workup, including imaging, is necessary to confirm a patient's diagnosis and initiate management in order to prevent further complications.
Copyright© the College of Family Physicians of Canada.
Figures

References
-
- Wilson BS, Tucci DL, O’Donoghue GM, Merson MH, Frankish H.. A Lancet Commission to address the global burden of hearing loss. Lancet 2019;393(10186):2106-8. Epub 2019 Feb 28. - PubMed
-
- Feder K, Michaud D, Ramage-Morin P, McNamee J, Beauregard Y.. Prevalence of hearing loss among Canadians aged 20 to 79: audiometric results from the 2012/2013 Canadian Health Measures Survey. Health Rep 2015;26(7):18-25. - PubMed
-
- Castiglione A, Benatti A, Velardita C, Favaro D, Padoan E, Severi D, et al. . Aging, cognitive decline and hearing loss: effects of auditory rehabilitation and training with hearing aids and cochlear implants on cognitive function and depression among older adults. Audiol Neurootol 2016;21(Suppl 1):21-8. Epub 2016 Nov 3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
