Robotic Inguinal Hernia Repair Outcomes: Operative Time and Cost Analysis
- PMID: 33209013
- PMCID: PMC7646555
- DOI: 10.4293/JSLS.2020.00058
Robotic Inguinal Hernia Repair Outcomes: Operative Time and Cost Analysis
Abstract
Background: Robotic inguinal hernia repair is the latest iteration of minimally invasive herniorrhaphy. Previous studies have shown expedited learning curves compared to traditional laparoscopy, which may be offset by higher cost and longer operative time. We sought to compare operative time and direct cost across the evolving surgical practice of 10 surgeons in our healthcare system.
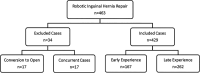
Methods: This is a retrospective review of all transabdominal preperitoneal robotic inguinal hernia repairs performed by 10 general surgeons from July 2015 to September 2018. Patients requiring conversion to an open procedure or undergoing simultaneous procedures were excluded. The data was divided to compare each surgeon's initial 20 cases to their subsequent cases. Direct operative cost was calculated based on the sum of supplies used intra-operatively. Multivariate analysis, using a generalized estimating equation, was adjusted for laterality and resident involvement to evaluate outcomes.
Results: Robotic inguinal hernia repairs were divided into two groups: early experience (n = 167) and late experience (n = 262). The late experience had a shorter mean operative time by 17.6 min (confidence interval: 4.06 - 31.13, p = 0.011), a lower mean direct operative cost by $538.17 (confidence interval: 307.14 - 769.20, p < 0.0001), and fewer postoperative complications (p = 0.030) on multivariate analysis. Thirty-day readmission rates were similar between both groups.
Conclusion: Increasing surgeon experience with robotic inguinal hernia repair is associated with a predictable reduction in operative time, complication rates, and direct operative cost per case. Thirty-day readmission rates are not affected by the learning curve.
Keywords: Cost; Inguinal hernia; Learning curve; Operative time; Robotic.
© 2020 by JSLS, Journal of the Society of Laparoscopic & Robotic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Bogdan Protyniak, MD, is a consultant for Intuitive Surgical, Inc.
Similar articles
-
Comparison of robotic versus laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) inguinal hernia repair.J Robot Surg. 2016 Sep;10(3):239-44. doi: 10.1007/s11701-016-0580-1. Epub 2016 Apr 25. J Robot Surg. 2016. PMID: 27112781
-
Contemporary inguinal hernia repair: do cost and operative time still differ by approach?Surg Endosc. 2025 Jun;39(6):3587-3591. doi: 10.1007/s00464-025-11722-4. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Surg Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40259091
-
Robotic Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Large Health System's Experience With the First 300 Cases and Review of the Literature.J Surg Res. 2019 Mar;235:98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2018.09.070. Epub 2018 Oct 25. J Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 30691857 Review.
-
Economic assessment of starting robot-assisted laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair in a single-centre retrospective comparative study: the EASTER study.BJS Open. 2021 Jan 8;5(1):zraa046. doi: 10.1093/bjsopen/zraa046. BJS Open. 2021. PMID: 33609369 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic TAPP inguinal hernia repair: lessons learned from 97 cases.Rev Col Bras Cir. 2021 Jan 29;48:e20202704. doi: 10.1590/0100-6991e-20202704. eCollection 2021. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2021. PMID: 33533825 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current status and future perspectives of robotic inguinal hernia repair.Surg Today. 2022 Oct;52(10):1395-1404. doi: 10.1007/s00595-021-02413-3. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Surg Today. 2022. PMID: 34860300 Review.
-
Earlier Experience of Robotic Inguinal Hernia Repair With the New Hugo™ Robotic System in Europe.J Abdom Wall Surg. 2025 Mar 31;4:13880. doi: 10.3389/jaws.2025.13880. eCollection 2025. J Abdom Wall Surg. 2025. PMID: 40248047 Free PMC article.
-
A New Modified Hysteroscopic-Laparoscopic Surgery for Cesarean Scar Pregnancy of Stable Type III.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Jun 3;14:2289-2295. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S308768. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34113158 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term quality of life outcomes following robotic inguinal hernioplasty: a single-centre experience of 100 cases.J Robot Surg. 2025 Apr 15;19(1):160. doi: 10.1007/s11701-025-02317-1. J Robot Surg. 2025. PMID: 40234268 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of operative times in bariatric surgery on outcomes: a matched analysis of the MBSAQIP database.Surg Endosc. 2023 Jun;37(6):4113-4122. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-09927-6. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 36752855 Review.
References
-
- Vossler JD, Pavlosky KK, Murayama SM, Moucharite MA, Murayama KM, Mikami DJ. Predictors of robotic versus laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. J Surg Res. 2019, 241:247–253. - PubMed
-
- Waite KE, Herman MA, Doyle PJ. Comparison of robotic versus laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) inguinal hernia repair. J Robot Surg. 2016, 10(3):239–244. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical