Protection Against Ionizing Radiation-Induced Normal Tissue Damage by Resveratrol: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33209085
- PMCID: PMC7651762
- DOI: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2020.20143
Protection Against Ionizing Radiation-Induced Normal Tissue Damage by Resveratrol: A Systematic Review
Abstract
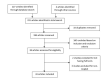
The use of some agents as radioprotectors has been evaluated for protection against normal tissue toxicity following exposure to ionizing radiation. Resveratrol, a natural flavonoid, with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties has attracted research interests for its radioprotective potential. This study systematically evaluates existing studies to examine the radioprotective effectiveness of resveratrol. A literature search of the electronic databases, including PubMed, Scopus, and Embase was conducted to retrieve articles investigating the protective effect of resveratrol against ionizing radiation-induced damage to normal tissues. The search timeframe ranged from the inception of each database to January 2020. From an initial search of 231 articles, and after the removal of duplicates as well as applying the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria, 33 articles were finally included for this systematic review. Results showed promising protective effect of resveratrol against ionizing radiation-induced damage to normal tissues. Furthermore, no adverse effect was observed after administering resveratrol. Resveratrol showed the potential to protect against ionizing radiation-induced damage to normal tissue cells via notable mechanisms, including anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects. However, further studies on the efficacy of clinical translation of resveratrol would open up more insights, while other gray areas such as the optimal radioprotective dosage of resveratrol requires further investigation. Overall, resveratrol is a potential double-edged sword in cancer therapy while protecting healthy tissues.
Keywords: DNA damage; Resveratrol; ionizing radiation; radiation protection.
©Copyright 2020 by the Atatürk University School of Medicine - Available online at www.eurasianjmed.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Berger EM. The Chernobyl disaster, concern about the environment, and life satisfaction. Kyklos. 2010;63:1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6435.2010.00457.x. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources