The rare entity of bilateral and unilateral neuroendocrine metastases to the breast: a case series and literature review
- PMID: 33209114
- PMCID: PMC7652541
- DOI: 10.3332/ecancer.2020.1123
The rare entity of bilateral and unilateral neuroendocrine metastases to the breast: a case series and literature review
Abstract
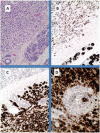
Introduction: Primary neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) in the breast are very rare. Until 2011, the prevalence was 0.1% of all breast lesions and 1% of all NENs, whereas metastatic breast NENs represent 1%-2% of all breast tumours. However, it seems that over the last 5 years the diagnostic frequency of breast NENs has increased, probably for more alert specialists and advanced diagnostic tools, leading to a prevalence of 2%-5% of diagnosed breast cancers, mostly in the elderly population. Breast metastases from extramammary malignancies are uncommon and bilateral ones are even more uncommon, with few reported in the literature. We describe four clinical settings of breast metastases from different NENs and the multidisciplinary approach for diagnosis and treatment.
Methods: Four patients were found to have NEN primaries metastasised to the breast. A literature review was conducted to identify similar cases and characterise breast metastases from neuroendocrinal tumors (NETs).
Results: Two patients presented with bilateral breast metastases (one with well-differentiated panNET and another with atypical lung carcinoid) and two had unilateral (one with moderately differentiated lung NET and one with atypical lung carcinoid). There are about 13 cases of NEN breast metastases reported in the English literature. The ileum is the most common primary site, followed by the appendix, duodenum, pancreas and lung.
Conclusion: Breast lesions from extramammary primary often pose a diagnostic challenge, since a breast nodule can be the first and often the only presentation of the disease. However, differentiating between primary and secondary NEN breast lesions is essential, owing to different clinical management and prognosis.
Keywords: bilateral; breast metastases; neuroendocrine; neuroendocrine neoplasms; neuroendocrine tumours.
© the authors; licensee ecancermedicalscience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Non-metastatic primary neuroendocrine neoplasms of the breast: a reference cancer center's experience of a heterogenous entity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 May 10;15:1217495. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1217495. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38800480 Free PMC article.
-
Pituitary metastases from neuroendocrine neoplasms: case report and narrative review.Pituitary. 2021 Oct;24(5):828-837. doi: 10.1007/s11102-021-01178-9. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Pituitary. 2021. PMID: 34342837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Primary Orbital Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs): Systematic Literature Review and Clinical Case Presentation.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 6;12(2):379. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020379. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38397981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological features and prognosis of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms in a Chinese population: a large, retrospective single-centre study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2017 Jul 13;17(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12902-017-0190-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2017. PMID: 28705205 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The role of multimodal treatment in patients with advanced lung neuroendocrine tumors.J Thorac Dis. 2017 Nov;9(Suppl 15):S1501-S1510. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.06.14. J Thorac Dis. 2017. PMID: 29201453 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bilateral breast metastases as the first manifestation of an occult pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor.Radiol Case Rep. 2021 Oct 7;16(12):3807-3814. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2021.09.008. eCollection 2021 Dec. Radiol Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34745398 Free PMC article.
-
Radiological and Histological Clues in the Diagnosis of Solitary and Synchronous Breast Metastasis From Small Cell Lung Carcinoma.J Breast Cancer. 2023 Apr;26(2):201-206. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2023.26.e20. J Breast Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37095620 Free PMC article.
-
Non-metastatic primary neuroendocrine neoplasms of the breast: a reference cancer center's experience of a heterogenous entity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 May 10;15:1217495. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1217495. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38800480 Free PMC article.
-
The rare case of synchronous bilateral breast metastasis from a lung neuroendocrine tumor (small cell lung carcinoma): a case report and literature review.Surg Case Rep. 2024 Sep 18;10(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s40792-024-01877-y. Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39292386 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Breast Neuroendocrine Tumors: An Analysis of the National Cancer Database.Ann Surg Oncol. 2022 Oct;29(10):6339-6346. doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-12123-w. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Ann Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35789311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin AL, Kong AL. Metastatic neuroendocrine tumor found on screening mammogram. WMJ. 2011;110(3):140–143. quiz 5. - PubMed
-
- Narese D, Virzi V, Narese F, et al. Breast core biopsy of a rare case of unknown primary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma metastatic to the breast. Clin Ter. 2014;165(6):302–304. - PubMed
