Arachidonic acid induces ER stress and apoptosis in HT-29 human colon cancer cells
- PMID: 33209199
- PMCID: PMC7646553
- DOI: 10.1080/19768354.2020.1813805
Arachidonic acid induces ER stress and apoptosis in HT-29 human colon cancer cells
Abstract
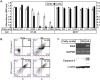
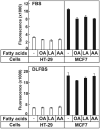
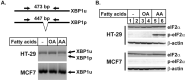
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have important functions in biological systems. The beneficial effects of dietary PUFAs against inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders have been shown. Studies using cancer cells have presented the anti-tumorigenic effects of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an n-3 PUFA, while arachidonic acid (AA), an n-6 PUFA, has been shown to elicit both pro- and anti-tumorigenic effects. In the current study, the anti-tumorigenic effects of AA were evaluated in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Upon adding AA in the media, more than 90% of HT-29 cells died, while the MCF7 cells showed good proliferation. AA inhibited the expression of SREBP-1 and its target genes that encode enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis. As HT-29 cells contained lower basal levels of fatty acid synthase, a target gene of SREBP-1, than that in MCF7 cells, the inhibitory effects of AA on the fatty acid synthase levels in HT-29 cells were much stronger than those in MCF-7 cells. When oleic acid (OA), a monounsaturated fatty acid that can be synthesized endogenously, was added along with AA, the HT-29 cells were able to proliferate. These results suggested that HT-29 cells could not synthesize enough fatty acids for cell division in the presence of AA because of the suppression of lipogenesis. HT-29 cells may incorporate more AA into their membrane phospholipids to proliferate, which resulted in ER stress, thereby inducing apoptosis. AA could be used as an anti-tumorigenic agent against cancer cells in which the basal fatty acid synthase levels are low.
Keywords: Arachidonic acid; ER stress; HT-29 cells; anti-tumorigenic effect.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
