Determinants of unmet need for family planning among married women in Zambia
- PMID: 33209230
- PMCID: PMC7649728
- DOI: 10.4081/jphia.2020.1084
Determinants of unmet need for family planning among married women in Zambia
Abstract
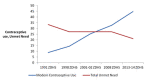
Unmet need for family planning remains a major family planning problem in most countries around the world. It presents serious consequences for the women, their families and society at large. This study was undertaken to establish the factors that affect total unmet needs for family planning and its components in Zambia. This study used the 2013/14 Zambia Demographic Health Survey (ZDHS) dataset focusing on currently married women aged 15 to 49. Data analysis took the form of descriptive, binary logistic and multinomial logistic regressions. The study shows that, although there has been a substantial increase in the use of contraceptives, combined unmet need for family planning has only decreased slightly over time, and currently stand at 21%, made up of 14% limiters and 7% spacers. Various factors were identified as determinants of unmet need for spacing, limiting or total unmet need for family planning. These included age, partner's level of education, contraceptive side effects, husband opposition to contraceptives and number of living children. To enhance utilization, policy should not be blind to the respective factors that influence combined unmet needs for spacing and limiting.
Keywords: Unmet need; Zambia; family planning; limiting; spacing; women.
©Copyright: the Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Central Statistical Office (CSO) [Zambia] Ministry of Health (MOH) ICF International. Zambia Demographic and Health Survey 2013-14. Rockville, Maryland, USA; 2014.
-
- United Nations. World Family Planning 2017 – Highlights. Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division; 2017. (ST/ESA/ SER.A/414).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources