Linezolid to treat urinary tract infections caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus
- PMID: 33209303
- PMCID: PMC7645773
- DOI: 10.1177/2050312120970743
Linezolid to treat urinary tract infections caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus
Abstract
Background: Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus can cause urinary tract infection. Linezolid possesses antimicrobial activity against vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus but has limited urinary excretion. Minimal data demonstrate efficacy of linezolid for treatment of urinary tract infections.
Objective: The main aim of this study is to compare post-treatment outcomes of linezolid to other antibiotics with vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus activity in the treatment of urinary tract infection caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus.
Methods: A retrospective cohort of inpatients within Veterans Health Administration facilities with urinary tract infection caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus was created. Patients with vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus isolated from urine cultures and chart documentation meeting criteria for urinary tract infection were identified. Demographics, comorbidity, treatments, and post-treatment outcomes were extracted from the electronic health record. Outcomes were compared between patients treated with linezolid and alternative antibiotics possessing vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus activity 14 days after treatment completion. Logistic regression adjusted for covariates associated with each outcome.
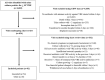
Results: Of 4,683 patients with a positive vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus culture, 624 (13%) met criteria for chart review, and 92 (15%) had documentation of urinary tract infection symptoms and treatment. The primary reason for exclusion was asymptomatic bacteriuria (64%). Patients had high Charlson Comorbidity Scores (mean = 8.7; standard deviation (SD) = 3.3), and 70% were located on general medical/surgical wards on the day of culture collection. Linezolid was prescribed in 54 (59%) cases. No difference between linezolid and comparator antibiotics were observed in re-initiation of antibiotics for vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus urinary tract infection (9% and 5% respectively (p = 0.56), (adjusted odds ratio (OR) = 1.90; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.34-10.63)), recurrent positive vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus culture (4% and 11%, respectively (p = 0.23), (adjusted OR = 0.36; 95% CI = 0.05-2.31)), or mortality (7% and 3%, respectively (p = 0.39) (adjusted OR = 2.96; 95% CI = 0.37-41.39)).
Conclusion: Most patients with vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus identified on urine culture were asymptomatic. Linezolid appears effective as comparator antibiotics for the treatment of mild vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus urinary tract infection.
Keywords: Enterococcus; Infectious diseases; antibiotic resistance; linezolid; urinary tract infections.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Hamada Y, Magarifuchi H, Oho M, et al. Clinical features of enterococcal bacteremia due to ampicillin-susceptible and ampicillin-resistant enterococci: an eight-year retrospective comparison study. J Infect Chemother 2015; 21(7): 527–530. - PubMed
-
- Wong AH, Wenzel RP, Edmond MB. Epidemiology of bacteriuria caused by vancomycin-resistant enterococci—a retrospective study. Am J Infect Control 2000; 28(4): 277–281. - PubMed
-
- Zyvox (linezolid) prescribing information. New York: Pharmacia and Upjohn, 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

