Advances in long-wavelength native phasing at X-ray free-electron lasers
- PMID: 33209311
- PMCID: PMC7642782
- DOI: 10.1107/S2052252520011379
Advances in long-wavelength native phasing at X-ray free-electron lasers
Abstract
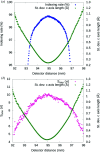
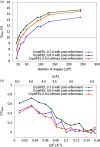
Long-wavelength pulses from the Swiss X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) have been used for de novo protein structure determination by native single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (native-SAD) phasing of serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) data. In this work, sensitive anomalous data-quality indicators and model proteins were used to quantify improvements in native-SAD at XFELs such as utilization of longer wavelengths, careful experimental geometry optimization, and better post-refinement and partiality correction. Compared with studies using shorter wavelengths at other XFELs and older software versions, up to one order of magnitude reduction in the required number of indexed images for native-SAD was achieved, hence lowering sample consumption and beam-time requirements significantly. Improved data quality and higher anomalous signal facilitate so-far underutilized de novo structure determination of challenging proteins at XFELs. Improvements presented in this work can be used in other types of SFX experiments that require accurate measurements of weak signals, for example time-resolved studies.
Keywords: X-ray free-electron lasers; anomalous data-quality indicators; de novo protein structure determination; serial femtosecond crystallography; single-wavelength anomalous diffraction.
© Karol Nass et al. 2020.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pink-beam serial femtosecond crystallography for accurate structure-factor determination at an X-ray free-electron laser.IUCrJ. 2021 Sep 23;8(Pt 6):905-920. doi: 10.1107/S2052252521008046. eCollection 2021 Nov 1. IUCrJ. 2021. PMID: 34804544 Free PMC article.
-
Protein structure determination by single-wavelength anomalous diffraction phasing of X-ray free-electron laser data.IUCrJ. 2016 Mar 9;3(Pt 3):180-91. doi: 10.1107/S2052252516002980. eCollection 2016 May 1. IUCrJ. 2016. PMID: 27158504 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane protein structure determination by SAD, SIR, or SIRAS phasing in serial femtosecond crystallography using an iododetergent.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Nov 15;113(46):13039-13044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1602531113. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27799539 Free PMC article.
-
[What Kind of Measurements Can Be Made with an X-ray Free Electron Laser at SACLA?].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022;142(5):479-485. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.21-00203-1. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022. PMID: 35491153 Review. Japanese.
-
Serial femtosecond crystallography at the SACLA: breakthrough to dynamic structural biology.Biophys Rev. 2018 Apr;10(2):209-218. doi: 10.1007/s12551-017-0344-9. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Biophys Rev. 2018. PMID: 29196935 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A modified phase-retrieval algorithm to facilitate automatic de novo macromolecular structure determination in single-wavelength anomalous diffraction.IUCrJ. 2024 Jul 1;11(Pt 4):587-601. doi: 10.1107/S2052252524004846. IUCrJ. 2024. PMID: 38904547 Free PMC article.
-
Pink-beam serial femtosecond crystallography for accurate structure-factor determination at an X-ray free-electron laser.IUCrJ. 2021 Sep 23;8(Pt 6):905-920. doi: 10.1107/S2052252521008046. eCollection 2021 Nov 1. IUCrJ. 2021. PMID: 34804544 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental phasing opportunities for macromolecular crystallography at very long wavelengths.Commun Chem. 2023 Oct 12;6(1):219. doi: 10.1038/s42004-023-01014-0. Commun Chem. 2023. PMID: 37828292 Free PMC article.
-
Pixel modelling - a new age in SFX data analysis.IUCrJ. 2020 Oct 30;7(Pt 6):949-950. doi: 10.1107/S2052252520014281. eCollection 2020 Nov 1. IUCrJ. 2020. PMID: 33209307 Free PMC article.
-
Pathways and Mechanism of Caffeine Binding to Human Adenosine A2A Receptor.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 27;8:673170. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.673170. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33987207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, P. D., Afonine, P. V., Bunkóczi, G., Chen, V. B., Davis, I. W., Echols, N., Headd, J. J., Hung, L.-W., Kapral, G. J., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., McCoy, A. J., Moriarty, N. W., Oeffner, R., Read, R. J., Richardson, D. C., Richardson, J. S., Terwilliger, T. C. & Zwart, P. H. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barends, T. R., Foucar, L., Ardevol, A., Nass, K., Aquila, A., Botha, S., Doak, R. B., Falahati, K., Hartmann, E., Hilpert, M., Heinz, M., Hoffmann, M. C., Kofinger, J., Koglin, J. E., Kovacsova, G., Liang, M., Milathianaki, D., Lemke, H. T., Reinstein, J., Roome, C. M., Shoeman, R. L., Williams, G. J., Burghardt, I., Hummer, G., Boutet, S. & Schlichting, I. (2015). Science, 350, 445–450. - PubMed
-
- Barends, T. R., Foucar, L., Botha, S., Doak, R. B., Shoeman, R. L., Nass, K., Koglin, J. E., Williams, G. J., Boutet, S., Messerschmidt, M. & Schlichting, I. (2014). Nature, 505, 244–247. - PubMed
-
- Barty, A., Caleman, C., Aquila, A., Timneanu, N., Lomb, L., White, T. A., Andreasson, J., Arnlund, D., Bajt, S., Barends, T. R., Barthelmess, M., Bogan, M. J., Bostedt, C., Bozek, J. D., Coffee, R., Coppola, N., Davidsson, J., Deponte, D. P., Doak, R. B., Ekeberg, T., Elser, V., Epp, S. W., Erk, B., Fleckenstein, H., Foucar, L., Fromme, P., Graafsma, H., Gumprecht, L., Hajdu, J., Hampton, C. Y., Hartmann, R., Hartmann, A., Hauser, G., Hirsemann, H., Holl, P., Hunter, M. S., Johansson, L., Kassemeyer, S., Kimmel, N., Kirian, R. A., Liang, M., Maia, F. R., Malmerberg, E., Marchesini, S., Martin, A. V., Nass, K., Neutze, R., Reich, C., Rolles, D., Rudek, B., Rudenko, A., Scott, H., Schlichting, I., Schulz, J., Seibert, M. M., Shoeman, R. L., Sierra, R. G., Soltau, H., Spence, J. C., Stellato, F., Stern, S., Struder, L., Ullrich, J., Wang, X., Weidenspointner, G., Weierstall, U., Wunderer, C. B. & Chapman, H. N. (2012). Nat. Photonics, 6, 35–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

