The synergism of B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) attenuated acute T-cell mediated rejection and prolonged renal graft survival
- PMID: 33209663
- PMCID: PMC7658142
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-20-728
The synergism of B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) attenuated acute T-cell mediated rejection and prolonged renal graft survival
Abstract
Background: Acute T-cell mediated rejection (TCMR) continues to be a major problem in the area of kidney transplantation. The B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) were recently found costimulatory molecules. The research aims to explore the inhibitory synergism of BTLA and CTLA-4 in TCMR.
Methods: We investigated the suppressive role of overexpressed BTLA and CTLA-4 in vitro. The rat kidney transplantation model was established to explore the effect of combined overexpressed BTLA and CTLA-4 in recipients of kidney transplantation. The grafts and peripheral blood were harvested for renal function, histology, immunohistochemical and flow cytometry analysis.
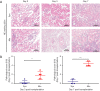
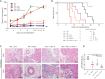
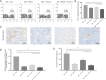
Results: Combination therapy decreased the secretion of interleukin-2 (IL-2) and proliferation of T cells compared to the single therapy and the control group. Decrease of interstitium monocyte infiltration and especially intimal arteritis in the graft was observed with the combination therapy, with remarkable reduction of numbers and proliferation response of T cells in peripheral blood and grafts. Combined overexpressed BTLA and CTLA-4 attenuated the acute TCMR after kidney transplantation and improved the graft function and prolonged the graft survival. The inhibiting role against TCMR in the combination therapy group was more effective than single therapy.
Conclusions: The synergism of BTLA and CTLA-4 attenuated acute TCMR after kidney transplantation by suppressing T cell activation and proliferation.
Keywords: Kidney transplantation; animal model; graft rejection; graft survival; immunosuppression.
2020 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tau-20-728). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Haas M, Loupy A, Lefaucheur C, et al. The Banff 2017 Kidney Meeting Report: Revised diagnostic criteria for chronic active T cell-mediated rejection, antibody-mediated rejection, and prospects for integrative endpoints for next-generation clinical trials. Am J Transplant 2018;18:293-307. 10.1111/ajt.14625 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
