Retrospective comparison of focused shockwave therapy and radial wave therapy for men with erectile dysfunction
- PMID: 33209675
- PMCID: PMC7658170
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-20-911
Retrospective comparison of focused shockwave therapy and radial wave therapy for men with erectile dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Low-intensity shockwave therapy (SWT) is an emerging treatment for erectile dysfunction (ED). Devices used for SWT include focused shockwave therapy (fSWT) or radial wave therapy (rWT), which differ in how the waves are generated, their tissue penetration, and the shape of their pressure waves. Most studies of SWT for ED to date have utilized fSWT. Although widely used, the efficacy of rWT for ED is unknown. Our objective is to compare the efficacy of rWT and fSWT for ED at our institution.
Methods: A retrospective chart review was performed to identify all men with ED treated by fSWT or rWT. Men with history suggesting non-vasculogenic ED were excluded. All men received 6 consecutive weekly treatments. The fSWT group received 3,000 shocks per treatment at 0.09 mJ/mm2. The rWT group received 10,000 shocks per treatment at 90 mJ and 15 Hz. Pre-treatment and 6-week post-treatment Sexual Health Inventory in Men (SHIM) scores were measured. Treatment response was categorized on a scale of 1-3 (1 if no improvement, 2 if erections sufficient for intercourse with phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (PDE5i), or 3 if sufficient erections without PDE5i). Primary endpoint was self-reported improvement score of 2 or greater.
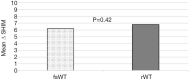
Results: A total of 48 men were included: 24 treated by fSWT and 24 by rWT. There were no significant differences in age, duration of ED, pre-treatment PDE5i use, or pre-treatment SHIM scores between the groups. Following treatment with rWT, the mean SHIM score improved from 9.3 to 16.1 (P<0.001). The mean SHIM following fSWT improved from 9.3 to 15.5 (P<0.001). The mean improvement in SHIM score did not differ between rWT (6.8) and fSWT (6.2) (P=0.42). 54% of men treated by fSWT experienced a significant clinical improvement (≥ grade 2 response) compared to 75% in the rWT group (P=0.42). There were no reported side effects with either device.
Conclusions: In our patient population, both fSWT and rWT were moderately effective treatments for arteriogenic ED with no observable difference in efficacy between the two modalities.
Keywords: Low-intensity shockwave therapy (low-intensity SWT); erectile dysfunction (ED); focused shockwave therapy (fSWT); radial shockwave therapy.
2020 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tau-20-911). DAS serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Translational Andrology and Urology from Dec 2017 to Jul 2022. DAS reports investment from Triurol, paid consultant from UroGen, outside the submitted work. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative effectiveness radial shockwave therapy versus focused linear shockwave therapy as an erectile dysfunction treatment systematic review and meta-analysis.Urol Ann. 2025 Apr-Jun;17(2):84-91. doi: 10.4103/ua.ua_13_25. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Urol Ann. 2025. PMID: 40352088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radial wave therapy does not improve early recovery of erectile function after nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy: a prospective trial.Transl Androl Urol. 2023 Feb 28;12(2):209-216. doi: 10.21037/tau-22-310. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Transl Androl Urol. 2023. PMID: 36915873 Free PMC article.
-
Shockwave Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction: Which Gives the Best Results? A Retrospective National, Multi-Institutional Comparative Study of Different Shockwave Technologies.Surg Technol Int. 2022 May 19;40:213-218. doi: 10.52198/22.STI.40.UR1556. Surg Technol Int. 2022. PMID: 35362088
-
Long-term effectiveness and predictors of success of low-intensity shockwave therapy in phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors non-responders.Arab J Urol. 2019 Nov 11;18(1):54-58. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2019.1688072. eCollection 2020. Arab J Urol. 2019. PMID: 32082635 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction in Diabetic Patients.Sex Med Rev. 2021 Oct;9(4):619-627. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2019.06.007. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Sex Med Rev. 2021. PMID: 31378506 Review.
Cited by
-
Restorative Therapies for Erectile Dysfunction: Position Statement From the Sexual Medicine Society of North America (SMSNA).Sex Med. 2021 Jun;9(3):100343. doi: 10.1016/j.esxm.2021.100343. Epub 2021 May 14. Sex Med. 2021. PMID: 34000480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (rESWT) on the Skin Surface Temperature of the Longissimus Dorsi Muscle in Clinically Healthy Racing Thoroughbreds: A Preliminary Study.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jun 18;13(12):2028. doi: 10.3390/ani13122028. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370538 Free PMC article.
-
Radial Type Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Enhances Penile Microvascular Perfusion in an Aging Rat Model: A Novel Interventional Strategy to Treat Erectile Dysfunction.World J Mens Health. 2025 Apr;43(2):396-406. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.240032. Epub 2024 May 30. World J Mens Health. 2025. PMID: 38863376 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Penile Low-Intensity Shockwave Therapy and Determinants of Treatment Response in Taiwanese Patients with Erectile Dysfunction.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 12;9(11):1670. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111670. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829899 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effectiveness radial shockwave therapy versus focused linear shockwave therapy as an erectile dysfunction treatment systematic review and meta-analysis.Urol Ann. 2025 Apr-Jun;17(2):84-91. doi: 10.4103/ua.ua_13_25. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Urol Ann. 2025. PMID: 40352088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Srini VS, Reddy RK, Shultz T, et al. Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for erectile dysfunction: A study in an Indian population. Can J Urol 2015;22:7614-22. - PubMed
-
- Costa P, Dias J, Gouveia R, et al. Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy on erectile dysfunction—first results from a prospective study. AME Med J 2019;4:32. 10.21037/amj.2019.06.03 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
