Biological applications of copper-containing materials
- PMID: 33210018
- PMCID: PMC7647998
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.09.017
Biological applications of copper-containing materials
Abstract
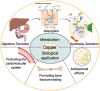
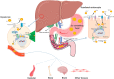
Copper is an indispensable trace metal element in the human body, which is mainly absorbed in the stomach and small intestine and excreted into the bile. Copper is an important component and catalytic agent of many enzymes and proteins in the body, so it can influence human health through multiple mechanisms. Based on the biological functions and benefits of copper, an increasing number of researchers in the field of biomaterials have focused on developing novel copper-containing biomaterials, which exhibit unique properties in protecting the cardiovascular system, promoting bone fracture healing, and exerting antibacterial effects. Copper can also be used in promoting incisional wounds healing, killing cancer cells, Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging, radioimmunological tracing and radiotherapy of cancer. In the present review, the biological functions of copper in the human body are presented, along with an overview of recent progress in our understanding of the biological applications and development of copper-containing materials. Furthermore, this review also provides the prospective on the challenges of those novel biomaterials for future clinical applications.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Antibacterial; Biomaterials; Copper; Osteogenesis.
© 2020 [The Author/The Authors].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biological properties of copper-doped biomaterials for orthopedic applications: A review of antibacterial, angiogenic and osteogenic aspects.Acta Biomater. 2020 Nov;117:21-39. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.09.044. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 33007487 Review.
-
Advances in copper-containing biomaterials for managing bone-related diseases.Regen Biomater. 2025 Mar 18;12:rbaf014. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbaf014. eCollection 2025. Regen Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40259976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copper-based biomaterials for bone and cartilage tissue engineering.J Orthop Translat. 2021 May 19;29:60-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2021.03.003. eCollection 2021 Jul. J Orthop Translat. 2021. PMID: 34094859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copper incorporated biomaterial-based technologies for multifunctional wound repair.Theranostics. 2024 Jan 1;14(2):547-570. doi: 10.7150/thno.87193. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38169658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An osteogenesis/angiogenesis-stimulation artificial ligament for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Acta Biomater. 2017 May;54:399-410. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.03.014. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28315493
Cited by
-
Antibacterial performance of a porous Cu-bearing titanium alloy by laser additive manufacturing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 3;11:1226745. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1226745. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37600307 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological, mechanical and antibacterial properties of Ti-Cu-N thin films deposited by sputtering DC.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 10;9(6):e17170. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17170. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37484339 Free PMC article.
-
Keratin/Copper Complex Electrospun Nanofibers for Antibacterial Treatments: Property Investigation and In Vitro Response.Materials (Basel). 2024 May 18;17(10):2435. doi: 10.3390/ma17102435. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38793501 Free PMC article.
-
Eco-Friendly Hydrogel Beads from Seashell Waste for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metals from Water.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Nov 23;16(23):3257. doi: 10.3390/polym16233257. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39684002 Free PMC article.
-
Health Risk Assessment of Toxic Metal(loids) Consumed Through Plant-Based Anti-diabetic Therapeutics Collected in the Northern Divisional City of Rajshahi, Bangladesh.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Apr;203(4):2149-2158. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04338-7. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 39129053
References
-
- Zhou X.-C., Yang F., Gong X.-Y., Zhao M., Zheng Y.-F., Sun Z.-L. New nitinol endovascular stent-graft system for abdominal aortic aneurysm with finite element analysis and experimental verification. Rare Met. 2019;38(6):495–502.
-
- Huang Y.-S., Huang H.-H. Effects of clinical dental implant abutment materials and their surface characteristics on initial bacterial adhesion. Rare Met. 2019;38(6):512–519.
-
- Li B.-Q., Li C.-L., Wang Z.-X., Lu X. Preparation of Ti–Nb–Ta–Zr alloys for load-bearing biomedical applications. Rare Met. 2019;38(6):571–576.
-
- Yuan Y., Jin S., Qi X., Chen X., Zhang W., Yang K., Zhong H. Osteogenesis stimulation by copper-containing 316L stainless steel via activation of akt cell signaling pathway and Runx2 upregulation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019;35(11):2727–2733.
-
- Jin S., Qi X., Wang T., Ren L., Yang K., Zhong H. In vitro study of stimulation effect on endothelialization by a copper bearing cobalt alloy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2018;106(2):561–569. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

