Effect of uric acid in animal models of ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33210575
- PMCID: PMC7983496
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X20967459
Effect of uric acid in animal models of ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
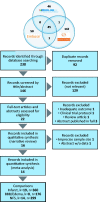
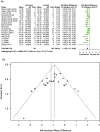
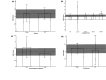
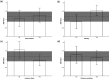
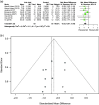
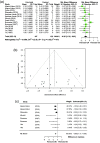
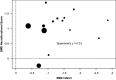
Addition of uric acid (UA) to thrombolytic therapy, although safe, showed limited efficacy in improving patients' stroke outcome, despite alleged neuroprotective effects of UA in preclinical research. This systematic review assessed the effects of UA on brain structural and functional outcomes in animal models of ischemic stroke. We searched Medline, Embase and Web of Science to identify 16 and 14 eligible rodent studies for qualitative and quantitative synthesis, respectively. Range of evidence met 10 of a possible 13 STAIR criteria. Median (Q1, Q3) quality score was 7.5 (6, 10) on the CAMARADES 15-item checklist. For each outcome, we used standardised mean difference (SMD) as effect size and random-effects modelling. Meta-analysis showed that UA significantly reduced infarct size (SMD: -1.18; 95% CI [-1.47, -0.88]; p < 0.001), blood-brain barrier (BBB) impairment/oedema (SMD: -0.72; 95% CI [-0.97, -0.48]; p < 0.001) and neurofunctional deficit (SMD: -0.98; 95% CI [-1.32, -0.63]; p < 0.001). Overall, there was low to moderate between-study heterogeneity and sizeable publication bias. In conclusion, published rodent data suggest that UA improves outcome following ischemic stroke by reducing infarct size, improving BBB integrity and ameliorating neurofunctional condition. Specific recommendations are given for further high-quality preclinical research required to better inform clinical research.
Keywords: animal model; brain damage; ischemic stroke; neurofunctional deficit; uric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect and mechanisms of resveratrol in animal models of ischemic stroke: A systematic review and Bayesian meta-analysis.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023 Dec;43(12):2013-2028. doi: 10.1177/0271678X231206236. Epub 2023 Oct 6. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023. PMID: 37802493 Free PMC article.
-
Emergent Uric Acid Treatment is Synergistic with Mechanical Recanalization in Improving Stroke Outcomes in Male and Female Rats.Neuroscience. 2018 Sep 15;388:263-273. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.07.045. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 30077000
-
Administration of Uric Acid in the Emergency Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016 Jan;16(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s11910-015-0604-7. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26711273 Review.
-
Statin Therapy in Ischemic Stroke Models: A Meta-Analysis.Transl Stroke Res. 2020 Aug;11(4):590-600. doi: 10.1007/s12975-019-00750-7. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Transl Stroke Res. 2020. PMID: 31788761 Review.
-
A pilot study of dual treatment with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and uric acid in acute ischemic stroke.Stroke. 2007 Jul;38(7):2173-5. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.106.480699. Epub 2007 May 24. Stroke. 2007. PMID: 17525395 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress, the blood-brain barrier and neurodegenerative diseases: The critical beneficial role of dietary antioxidants.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Oct;13(10):3988-4024. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.010. Epub 2023 Jul 16. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37799389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum uric acid and prognosis in acute ischemic stroke: a dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Sep 1;15:1223015. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1223015. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37727320 Free PMC article.
-
U-Shaped Association Between Serum Uric Acid and Hemorrhagic Transformation After Intravenous Thrombolysis.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2022;19(2):150-159. doi: 10.2174/1567202619666220707093427. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 35796447
-
Effect of Cilostazol in Animal Models of Cerebral Ischemia and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Neurocrit Care. 2023 Jun;38(3):698-713. doi: 10.1007/s12028-022-01637-6. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Neurocrit Care. 2023. PMID: 36450971
-
Association between uric acid and the risk of hemorrhagic transformation in patients with acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Jul 25;15:1378912. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1378912. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39119562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hankey GJ.Stroke. Lancet 2017; 389: 641–654. - PubMed
-
- Chamorro Á, Dirnagl U, Urra X, et al.. Neuroprotection in acute stroke: targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol 2016; 15: 869–881. - PubMed
-
- Becker BF.Towards the physiological function of uric acid. Free Radic Biol Med 1993; 14: 615–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

