The restorative effect of apocynin and catalase in l-arginine induced hypotension on normotensive subjects - the role of oxidative stress
- PMID: 33210935
- PMCID: PMC8549869
- DOI: 10.33549/physiolres.934426
The restorative effect of apocynin and catalase in l-arginine induced hypotension on normotensive subjects - the role of oxidative stress
Abstract
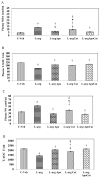
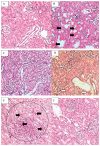
L-arginine is a substrate for nitric oxide synthase (NOS) responsible for the production of NO. This investigation studied the effect of apocynin, an NADPH oxidase inhibitor and catalase, an H2O2 scavenger on L-arginine induced oxidative stress and hypotension. Forty Wistar-Kyoto rats were treated for 14 days with vehicle, L-arginine (12.5mg/ml p.o.), L-arginine+apocynin (2.5mmol/L p.o.), L-arginine+catalase (10000U/kg/day i.p.) and L-arginine plus apocynin+catalase respectively. Weekly renal functional and hemodynamic parameters were measured and kidneys harvested at the end of the study for histopathological and renal NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4) assessments. L-arginine administration in normotensive rats decreased systolic blood pressure (120±2 vs 91±2mmHg) and heart rate (298±21 vs 254±15b/min), enhanced urinary output (21.5±4.2 vs 32±1.9ml/24h , increased creatinine clearance (1.72±0.56 vs 2.62±0.40ml/min/kg), and fractional sodium excretion (0.88±0.16 vs 1.18±0.16 %), caused proteinuria (28.10±1.93 vs 35.26±1.69mg/kg/day) and a significant decrease in renal cortical blood perfusion (292±3 vs 258±5bpu) and pulse wave velocity (3.72±0.20 vs 2.84±0.13m/s) (all P<0.05). L-arginine increased plasma malondialdehyde (by ~206 % P<0.05) and NO (by~51 %, P<0.05) but decreased superoxide dismutase (by~31 %, P<0.05) and total antioxidant capacity (by~35 %, P<0.05) compared to control. Renal Nox4 mRNA activity was approximately 2.1 fold higher (P<0.05) in the L-arginine treated rats but was normalized by apocynin and apocynin plus catalase treatment. Administration of apocynin and catalase, but not catalase alone to rats fed L-arginine, restored the deranged renal function and structure, prevented hypotension and enhanced the antioxidant capacity and suppressed Nox4 expression. These findings suggest that apocynin and catalase might be used prophylactically in states of oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of L-NAME-induced hypertension by combined treatment with apocynin and catalase: the role of Nox 4 expression.Physiol Res. 2021 Mar 17;70(1):13-26. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934497. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 33728924 Free PMC article.
-
Apocynin and catalase prevent hypertension and kidney injury in Cyclosporine A-induced nephrotoxicity in rats.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 16;15(4):e0231472. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231472. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32298299 Free PMC article.
-
Apocynin but not L-arginine prevents and reverses dexamethasone-induced hypertension in the rat.Am J Hypertens. 2006 Apr;19(4):413-8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2005.09.023. Am J Hypertens. 2006. PMID: 16580579
-
Apocynin attenuates oxidative stress and hypertension in young spontaneously hypertensive rats independent of ADMA/NO pathway.Free Radic Res. 2012 Jan;46(1):68-76. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2011.639069. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Free Radic Res. 2012. PMID: 22070348
-
Sex differences in oxidative stress and the impact on blood pressure control and cardiovascular disease.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007 Sep;34(9):938-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04643.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17645644 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of L-NAME-induced hypertension by combined treatment with apocynin and catalase: the role of Nox 4 expression.Physiol Res. 2021 Mar 17;70(1):13-26. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934497. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 33728924 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactivity-Guided Isolation and Antihypertensive Activity of Citrullus colocynthis Polyphenols in Rats with Genetic Model of Hypertension.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 23;59(10):1880. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101880. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893598 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and Subacute Oral Toxicity Assessment of The Polysaccharides Extracted from Clinacanthus nutans Leaves: A Preclinical Model for Drug Safety Screening.Trop Life Sci Res. 2025 Mar;36(1):245-276. doi: 10.21315/tlsr2025.36.1.13. Epub 2025 Mar 30. Trop Life Sci Res. 2025. PMID: 40567812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AHMAD A, SATTAR MA, RATHORE HA, ABDULLA MH, KHAN SA, ABDULLAH NA, JOHNS EJ. Enhanced expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the myocardium ameliorates the progression of left ventricular hypertrophy in L-arginine treated Wistar-Kyoto rats. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;67:31–44. - PubMed
-
- AHMAD A, SATTAR MA, RATHORE HA, ABDULLA MH, KHAN SA, AZAM M, ABDULLAH NA, JOHNS EJ. Up regulation of cystathione y lyase and hydrogen sulphide in the myocardium inhibits the progression of isoproterenol-caffeine induced left ventricular hypertrophy in Wistar Kyoto rats. PloS One. 2016;11:e0150137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150137. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- AHMAD FUD, SATTAR MA, RATHORE HA, TAN YC, AKHTAR S, JIN OH, PEI YP, ABDULLAH NA, JOHNS EJ. Hydrogen sulphide and tempol treatments improve the blood pressure and renal excretory responses in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Ren Fail. 2014;36:598–605. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2014.882218. - DOI - PubMed
