Non-invasive assessment of cirrhosis using multiphasic dual-energy CT iodine maps: correlation with model for end-stage liver disease score
- PMID: 33211150
- PMCID: PMC9282666
- DOI: 10.1007/s00261-020-02857-0
Non-invasive assessment of cirrhosis using multiphasic dual-energy CT iodine maps: correlation with model for end-stage liver disease score
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether multiphasic dual-energy (DE) CT iodine quantitation correlates with the severity of chronic liver disease.
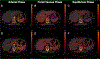
Methods: We retrospectively included 40 cirrhotic and 28 non-cirrhotic patients who underwent a multiphasic liver protocol DECT. All three phases (arterial, portal venous (PVP), and equilibrium) were performed in DE mode. Iodine (I) values (mg I/ml) were obtained by placing regions of interest in the liver, aorta, common hepatic artery, and portal vein (PV). Iodine slopes (λ) were calculated as follows: (Iequilibrium-Iarterial)/time and (Iequilibrium-IPVP)/time. Spearman correlations between λ and MELD scores were evaluated, and the area under the curve of the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) was calculated to distinguish cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients.
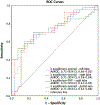
Results: Cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients had significantly different λequilibrium-arterial [IQR] for the caudate (λ = 2.08 [1.39-2.98] vs 1.46 [0.76-1.93], P = 0.007), left (λ = 2.05 [1.50-2.76] vs 1.51 [0.59-1.90], P = 0.002) and right lobes (λ = 1.72 [1.12-2.50] vs 1.13 [0.41-0.43], P = 0.003) and for the PV (λ = 3.15 [2.20-5.00] vs 2.29 [0.85-2.71], P = 0.001). λequilibrium-PVP were significantly different for the right (λ = 0.11 [- 0.45-1.03] vs - 0.44 [- 0.83-0.12], P = 0.045) and left lobe (λ = 0.30 [- 0.25-0.98] vs - 0.10 [- 0.35-0.24], P = 0.001). Significant positive correlations were found between MELD scores and λequilibrium-arterial for the caudate lobe (ρ = 0.34, P = 0.004) and λequilibrium-PVP for the caudate (ρ = 0.26, P = 0.028) and right lobe (ρ = 0.33, P = 0.007). AUROC in distinguishing cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients were 0.72 (P = 0.002), 0.71 (P = 0.003), and 0.75 (P = 0.001) using λequilibrium-arterial for the left lobe, right lobe, and PV, respectively. The λequilibrium-PVP AUROC of the right lobe was 0.73 (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Multiphasic DECT iodine quantitation over time is significantly different between cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients, correlates with the MELD score, and it could potentially serve as a non-invasive measure of cirrhosis and disease severity with acceptable diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: Chronic liver disease; Dual-energy CT; Iodine concentration; Liver cirrhosis; Material decomposition.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards
Figures

Similar articles
-
Liver fibrosis assessment with multiphasic dual-energy CT: diagnostic performance of iodine uptake parameters.Eur Radiol. 2021 Aug;31(8):5779-5790. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07706-2. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33768289
-
Noninvasive Staging of Liver Fibrosis Using 5-Minute Delayed Dual-Energy CT: Comparison with US Elastography and Correlation with Histologic Findings.Radiology. 2021 Mar;298(3):600-608. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021202232. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Radiology. 2021. PMID: 33399510
-
Spectral CT: preliminary studies in the liver cirrhosis.Korean J Radiol. 2012 Jul-Aug;13(4):434-42. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.434. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Korean J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22778565 Free PMC article.
-
Material decomposition using iodine quantification on spectral CT for characterising nodules in the cirrhotic liver: a retrospective study.Eur Radiol Exp. 2021 May 28;5(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s41747-021-00220-6. Eur Radiol Exp. 2021. PMID: 34046753 Free PMC article.
-
Doppler Ultrasound in Liver Cirrhosis: Correlation of Hepatic Artery and Portal Vein Measurements With Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Score.J Ultrasound Med. 2017 Apr;36(4):725-730. doi: 10.7863/ultra.16.03107. Epub 2016 Dec 27. J Ultrasound Med. 2017. PMID: 28026900
Cited by
-
Spectral CT: Current Liver Applications.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 May 9;13(10):1673. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13101673. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37238163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-invasive assessment of liver function in cirrhosis using iodine density difference between the portal vein and hepatic vein on spectral CT: correlation with Child-Pugh grades.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01768-0. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40596902 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

