Effect of physical activity promotion on adiponectin, leptin and other inflammatory markers in prediabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 33211181
- PMCID: PMC8053655
- DOI: 10.1007/s00592-020-01626-1
Effect of physical activity promotion on adiponectin, leptin and other inflammatory markers in prediabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Aims: Inflammatory stage in prediabetes is associated with increase in level of adipokines and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Physical activity promotion considered as a first-line therapeutic strategy to treat prediabetes. We have conducted the systematic review and meta-analysis to strengthen the evidence on the impact of physical activity promotion on inflammatory markers in prediabetes.
Methods: Studies were identified using electronic search and manual search techniques by choosing keywords for prediabetes, physical activity and inflammatory marker. Randomized controlled trials on individuals diagnosed with prediabetes and provided intervention in the form of physical activity were included in this review. Adiponectin, leptin, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-α were the considered outcome measures.
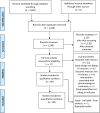
Results: Our search retrieved 1,688 citations, 31 full-text articles assessed for eligibility of inclusion. Nine studies satisfied the pre-specified criteria for inclusion. Meta-analysis found that physical activity with or without dietary or lifestyle modification reduces level of leptin (MD-2.11 ng/mL, 95% CI -3.81 - -0.42) and interleukin-6 (MD -0.15 pg/mL, 95% CI -0.25--0.04). It has no effect on level of adiponectin (MD 0.26 µg/mL, 95% CI -0.42- 0.93), C-reactive protein (MD -0.05 mg/L, 95% CI -0.33-0.23) and tumour necrosis factor-α (MD 0.67 pg/mL, 95% CI -2.56-3.89).
Conclusions: This review suggests that physical activity promotion with dietary and lifestyle modification may reduce the level of leptin and interleukin-6 but are uncertain if there is any effect on levels of adiponectin, C-reactive protein and tumour necrosis factor-α in the individuals with prediabetes.
Keywords: Adipokines; Cytokines; Diabetes; Inflammation; Lifestyle.
Conflict of interest statement
Ms. Radhika Aditya Jadhav, Dr. Arun G Maiya, Ms. Aditi Hombali, Dr. Shashikiran Umakanth and Dr. Shivashankar K N declared that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures



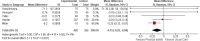

Similar articles
-
Carnosine Supplementation Has No Effect on Inflammatory Markers in Adults with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomised Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 15;16(22):3900. doi: 10.3390/nu16223900. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39599686 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of dairy products consumption on inflammatory biomarkers among adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Jun 9;30(6):872-888. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2020.01.011. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32409275
-
The impact of high-intensity interval training on inflammatory markers in metabolic disorders: A meta-analysis.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020 Nov;30(11):2020-2036. doi: 10.1111/sms.13754. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020. PMID: 32585734
-
Effects of a community-based weight loss intervention on adipose tissue circulating factors.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2014 Oct-Dec;8(4):205-11. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2014.09.003. Epub 2014 Oct 5. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2014. PMID: 25293442 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of vitamin D supplementation on selected inflammatory biomarkers in older adults: a secondary analysis of data from a randomised, placebo-controlled trial.Br J Nutr. 2015 Sep 14;114(5):693-9. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515002366. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Br J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26206095 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Daily Step Count and All-Cause Mortality: A Dose-Response Meta-analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies.Sports Med. 2022 Jan;52(1):89-99. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01536-4. Epub 2021 Aug 21. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 34417979
-
Integrated neuromuscular training intervention applied in schools induces a higher increase in salivary high molecular weight adiponectin and a more favorable body mass index, cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle strength in children as compared to the traditional physical education classes.Front Public Health. 2024 May 2;12:1337958. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1337958. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38756879 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Metabolic Alteration Bridging the Prediabetic State and Colorectal Cancer.Cells. 2024 Apr 9;13(8):663. doi: 10.3390/cells13080663. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38667278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of plant-based diets combined with exercise training on leptin and adiponectin levels in adults with or without chronic diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies.Front Nutr. 2024 Oct 9;11:1465378. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1465378. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39444577 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of 12-Week Traditional Thai Exercise (Ruesi Dadton) on Glycemic Control and Inflammatory Markers in Prediabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Life (Basel). 2023 Nov 5;13(11):2166. doi: 10.3390/life13112166. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADA - American Diabetes Association Diagnosis of diabetes and prediabetes. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:11–63.
-
- World Health Organization . Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia. Diabetes Mellitus: Report of a WHO Study; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

