Salivary diagnostics of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- PMID: 33211392
- PMCID: PMC7753835
- DOI: 10.1111/odi.13729
Salivary diagnostics of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
Abstract
Introduction: Laboratory testing for the SARS-CoV-2 virus and the consequent respiratory coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is categorized into methods that detect the viral presence and methods that detect antibodies produced in the host as a response to infection. Methods that detect viral presence into the host excretions measure current infection by SARS-CoV-2, whereas the detection of human antibodies exploited against SARS-CoV-2 evaluates the past exposure to the virus.
Objective: This review provides a comprehensive overview for the use of saliva as a specimen for the detection of SARS-CoV-2, the methods for the salivary diagnostics utilized till very recently, and the arisen considerations for the diagnosis of COVID-19 disease.
Conclusion: The major advantage of using saliva as a specimen for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 is that saliva collection is a non-invasive method which produces no discomfort to the patient and permits the patients to utilize home self-sampling techniques in order to protect health providers from the exposure to the pathogen. There is an urgent need to increase the active research for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in the saliva because the non-invasive salivary diagnostics may provide a reliable and cost-effective method suitable for the fast and early detection of COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; diagnosis; saliva; salivary diagnostics.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures
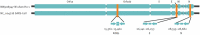
References
-
- Azzi, L. , Baj, A. , Alberio, T. , Lualdi, M. , Veronesi, G. , Carcano, G. , Ageno, W. , Gambarini, C. , Maffioli, L. , Saverio, S. D. , Gasperina, D. D. , Genoni, A. P. , Premi, E. , Donati, S. , Azzolini, C. , Grandi, A. M. , Dentali, F. , Tangianu, F. , Sessa, F. , … Fasano, M. (2020). Rapid Salivary Test suitable for a mass screening program to detect SARS‐CoV‐2: A diagnostic accuracy study. Journal of Infection, 81(3), e75–e78. 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.06.042 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azzi, L. , Carcano, G. , Gianfagna, F. , Grossi, P. , Gasperina, D. D. , Genoni, A. , Fasano, M. , Sessa, F. , Tettamanti, L. , Carinci, F. , Maurino, V. , Rossi, A. , Tagliabue, A. , & Baj, A. (2020). Saliva is a reliable tool to detect SARS‐CoV‐2. Journal of Infection, 81, e45–e50. 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beaubien, J. (2020). In age of COVID‐19, Hong Kong innovates to test and quarantine thousands. NPR.org. https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2020/02/23/808290390/in‐age‐of...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

