Final results of a phase 1 study of loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed/refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 33211842
- PMCID: PMC8138546
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020007512
Final results of a phase 1 study of loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed/refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
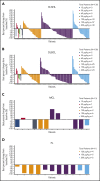
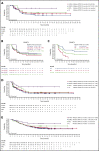
The prognosis for patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) remains poor, with a need for alternatives to current salvage therapies. Loncastuximab tesirine (ADCT-402) is an antibody-drug conjugate comprising a humanized anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody conjugated to a pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer toxin. Presented here are final results of a phase 1 dose-escalation and dose-expansion study in patients with R/R B-NHL. Objectives were to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and recommended dose(s) for expansion and evaluate safety, clinical activity, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity of loncastuximab tesirine. Overall, 183 patients received loncastuximab tesirine, with 3 + 3 dose escalation at 15 to 200 µg/kg and dose expansion at 120 and 150 µg/kg. Dose-limiting toxicities (all hematologic) were reported in 4 patients. The MTD was not reached, although cumulative toxicity was higher at 200 µg/kg. Hematologic treatment-emergent adverse events were most common, followed by fatigue, nausea, edema, and liver enzyme abnormalities. Overall response rate (ORR) in evaluable patients was 45.6%, including 26.7% complete responses (CRs). ORRs in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), mantle cell lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma were 42.3%, 46.7%, and 78.6%, respectively. Median duration of response in all patients was 5.4 months and not reached in patients with DLBCL (doses ≥120 µg/kg) who achieved a CR. Loncastuximab tesirine had good stability in serum, notable antitumor activity, and an acceptable safety profile, warranting continued study in B-NHL. The recommended dose for phase 2 was determined as 150 µg/kg every 3 weeks for 2 doses followed by 75 µg/kg every 3 weeks. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02669017.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


Comment in
-
A new warhead in lymphoma therapy?Blood. 2021 May 13;137(19):2568-2570. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020009782. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33983420 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Al-Hamadani M, Habermann TM, Cerhan JR, Macon WR, Maurer MJ, Go RS. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtype distribution, geodemographic patterns, and survival in the US: A longitudinal analysis of the National Cancer Data Base from 1998 to 2011. Am J Hematol. 2015;90(9):790-795. - PubMed
-
- Casulo C, Barr PM. How I treat early-relapsing follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2019;133(14):1540-1547. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7-34. - PubMed
-
- Sehn LH, Donaldson J, Chhanabhai M, et al. Introduction of combined CHOP plus rituximab therapy dramatically improved outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in British Columbia. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(22):5027-5033. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

